What are Units?
- Units are used to measure certain things.
- For example meters are used to measure distance and joules are used to measure energy or work.
S.I. Units
- There are seven fundamental S.I. units. All other units are derived from these.
- Other units of measurement are made from different combinations of fundamental units.
- Below is a list of the names of the units alongside their symbols.
- Mass: kilograms - kg
- Length: meters - m
- Time: second - s
- Temperature: Kelvin - K
- Amount of Substance: moles - mol
- Electric current: amperes or amps - A
- Luminous intensity: candela - cd
- S.I. units, and the entirety of the metric system are designed to be consistent and reasonable and are used internationally.
- Even in countries like the United States where the imperial system is more common, the metric system is still used in scientific studies and research.
Kilograms
- Kilograms define the mass of an object.
- Kilograms are generally used over grams (which is the base unit) due to most objects generally weighing a few kilograms or more.
- Mass is independent of gravitational force and should not be confused with weight, which is a separate measurement.
- Generally tonnes are used to notate 1000 kilograms. These shouldn't be used with the imperial tons which notate a slightly different mass (1 metric tonne ≈ 1.1 imperial tons).
- For consistency, megagrams can be used instead of tonnes as they both mean the same thing (and frankly "megagram" sounds a lot cooler).
Meters
- Meters are units designed to measure distance. The average adult is usually around 1.7 meters tall.
- Meter's are based around the circumference of the Earth. The Earth's circumference is almost exactly 40,000 meters (there is a small discrepancy due to measurements when meters were first defined).
Seconds
- Seconds are used to measure the passing of time.
- Time is one of the few measurements to use somewhat irregular units.
- Each step up is by 60, instead of by 10.
- This only applies to hours (60 min or 3600s) and minutes (60s).
- Scientific prefixes can still be used but you will see hours and minutes a lot more often.
Kelvin
- Kelvin is the measurement of temperature.
- It is similar to Celsius and increases or decreases proportionally to Celsius.
- Celsius and Kelvin rise with the same increments, although 0 Kelvin is -273.15 Celsius.
- Kelvin and Celsius can be inferred from one another by either adding or subtracting 273.15 Celsius.
- Temperature is based on the movement of atoms, with more heat making atoms vibrate more and vice versa.
- Absolute zero, or 0 Kelvin is when there is no heat vibration at all.
Moles
- Moles are a very large number, similar to a dozen or a pair.
- For example you could have a mole of bread like how you could have a dozen loaves of bread.
- Moles are used to represent the amount of particles in an amount of substance.
- Moles are important as other units such as kilograms or liters can't objectively measure the amount of substance because of the different densities and masses of substances.
- One mole is 6.022 • 10²³ particles (a reaaaaaaaally big number).
Amperes
- Electric current is used to connect electric phenomena (such as electric and magnetics) with mechanical forces.
- Electric current is the flow of charged particles through a conductor.
- Amperes and electric current shouldn't be confused with volts, which measure electric potential difference.
Candelas
- Candelas are used to measure luminous intensity. In other words they are the unit for the measurement of light.
Writing Units
- When notating other units, square brackets can be used.
- For example [v], would mean the unit of velocity, which is m/s or meters per second.
- In a scenario where larger units are needed, [v] = km/h would explain what velocity is.
- Although units generally always should be changed into the SI units.
- Thus it could be written as: [v] = 1000m/3600s.
Prefixes
- Prefixes can be added in front of units in order to show the amount, depending on if you're measuring larger or smaller quantities.
- For example kilo means 1000, thus a kilometer is 1000 meters.
- Below is a chart of all necessary metric prefixes. There are some additional ones but they are too miniscule to care about unless its specifically related to your field of study.
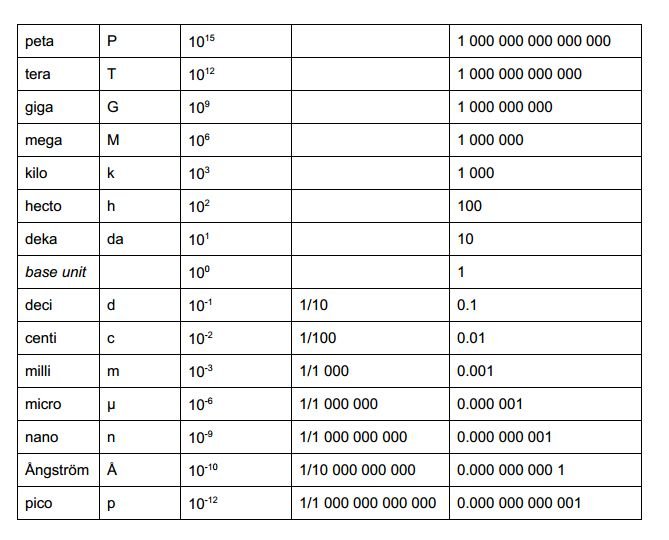
- For perspective, the nucleus of an atom is usually several femtometers, depending on the size of the atom.
