What is Torque?
- When applying force to certain objects, such as sitting on a see-saw, they do not move normally, but rotate instead.
- The force that causes this rotation is determined by torque.
- Torque, τ, is the force about an axis.
- It is calculated as:
τ = Frsinθ
- Where F is the force being applied, r is the distance from the turning point at which the force is applied, and θ is the angle from the surface of the lever arm and the vector of force.
- The "lever arm" is the surface being rotated, for example a wrench or a door.
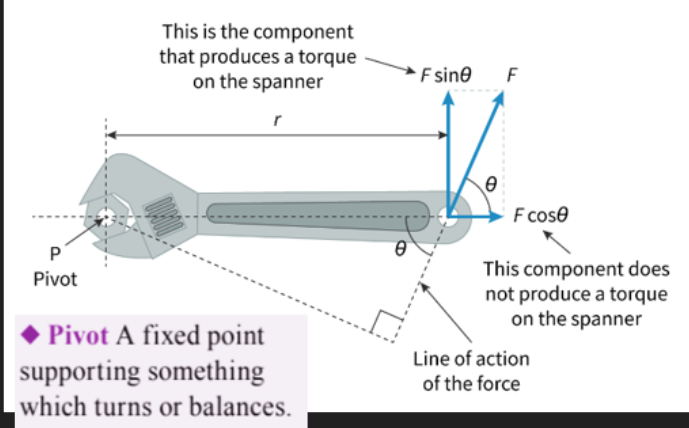
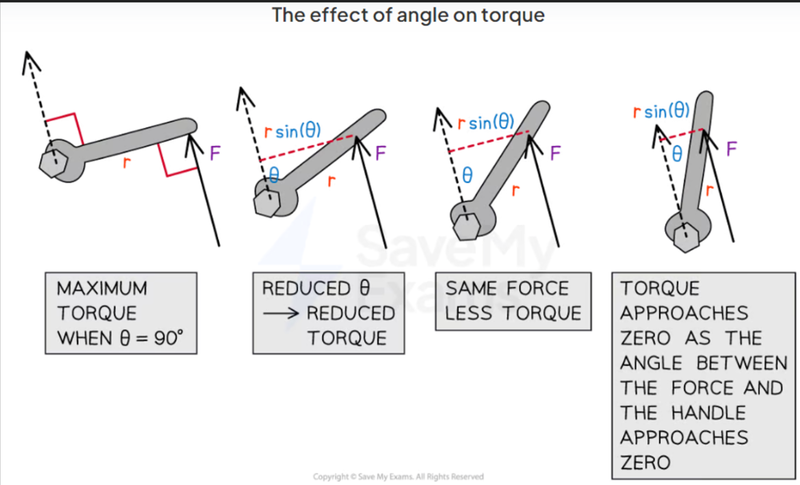
- As sinθ is greatest when θ=90°, the greatest torque is when the force applied is perpendicular to the lever.
- The greater the distance from the pivot, the greater the torque.
- That's why its a lot easier to turn a bolt with a wrench than with your hands, the wrench increases the distance with which force is applied, leading to greater torque.
- If there is no actual rotation, then the torque is called a "moment" of a force.
- The SI unit of torque is Nm, which is actually the same units that make up Joules.
- However, newton meters are used when referring to torque to differentiate it from energy.
Combining Torques
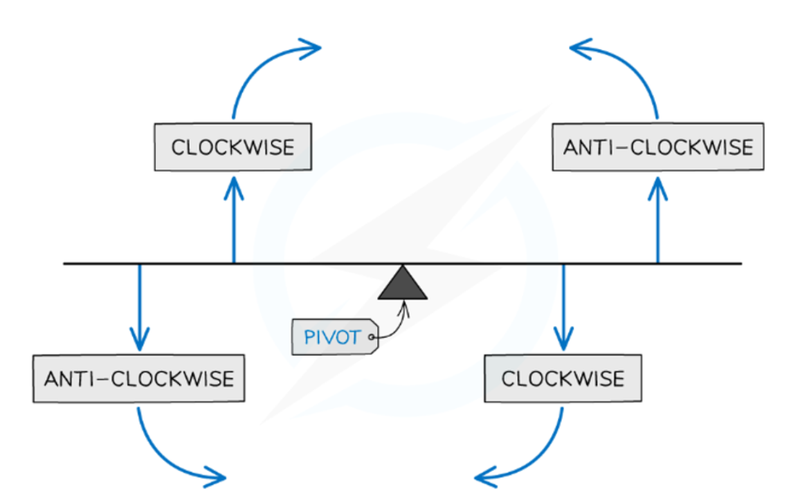
- As torque is a vector quantity, multiple torques adding on an object can be added together.
- Imagine that the object is split into two parts by the pivot point.
- If the torques on both sides would cause it to rotate in the same direction, then they are added together.
- However, if the torques would cause rotation in opposite directions, such as one causing clockwise rotation and the other anticlockwise rotation, then the torques are subtracted from one another.
- The total torque determines the direction the object rotates in.
Torque Couples
- A torque couple is a pair of equal and opposite coplanar forces that act to produce rotation only.
- Torque couples are always equal in magnitude, opposite in direction, on opposite sides of the object and perpendicular to the distance between them.
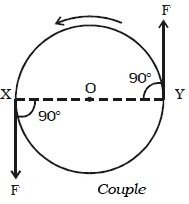
- Torque couples produce double the torque of one of the torques, as both are added together.
Rotational Equilibrium
- Bodies in rotational equilibrium have a resultant torque of zero.
- This means that the two torques cancel out and total torque is zero as the forces on either side of the lever are balanced.
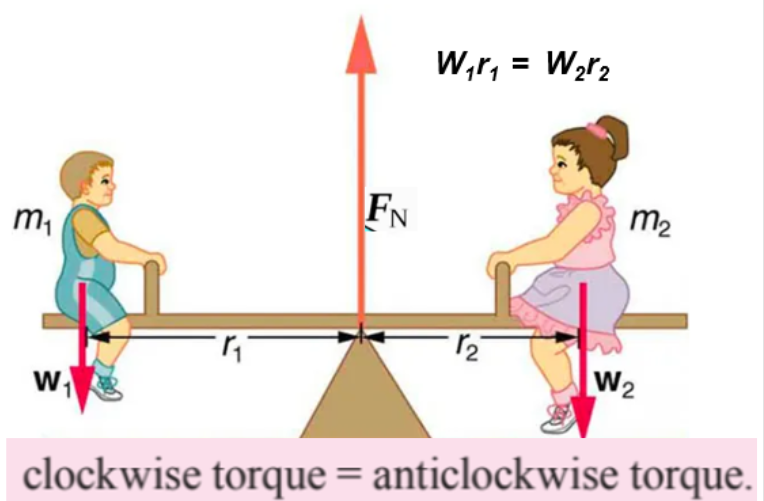
- Zero net torque is when two torques cancel each other, maintaining the body's original rotational state.
- Zero net forces mean that the forces on either side of the pivot nullify eachother.
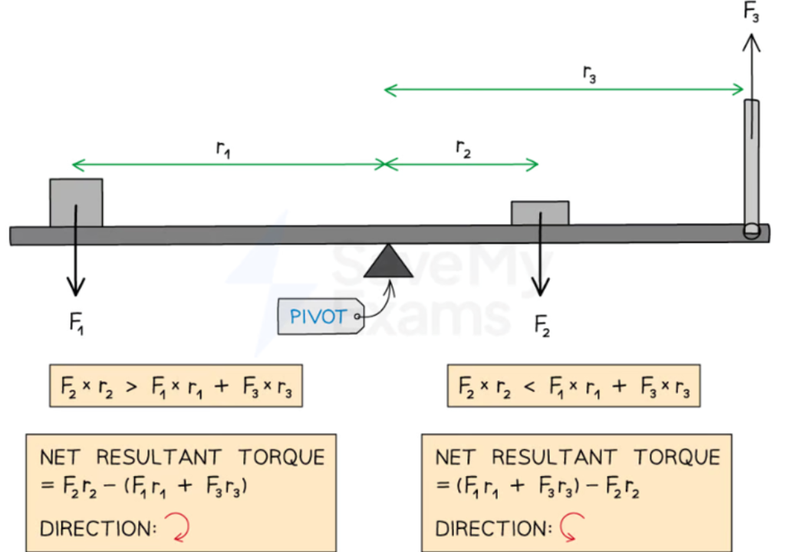
Unbalanced Torque
- If one of the sides produces greater torque than the other side, then it will overpower the other side, and the object will start rotating at an acceleration pace in the direction of the stronger torque.
Sources