What is the Greenhouse Effect?
- When solar radiation strikes a plane that has a gaseous atmosphere, the gases comprising the atmosphere can absorb infrared radiation (heat).
- The remainder of the incoming radiation then reaches the ground to either be scattered back into the atmosphere or absorbed.
- Solids can absorb all frequencies of radiation, and convert them into infrared wavelengths.
- The heated ground can then emit infrared radiation back into the atmosphere, which then intercepts more energy on the way out.
- The result is that the atmosphere traps heat and causes the temperature of the planet to rise.
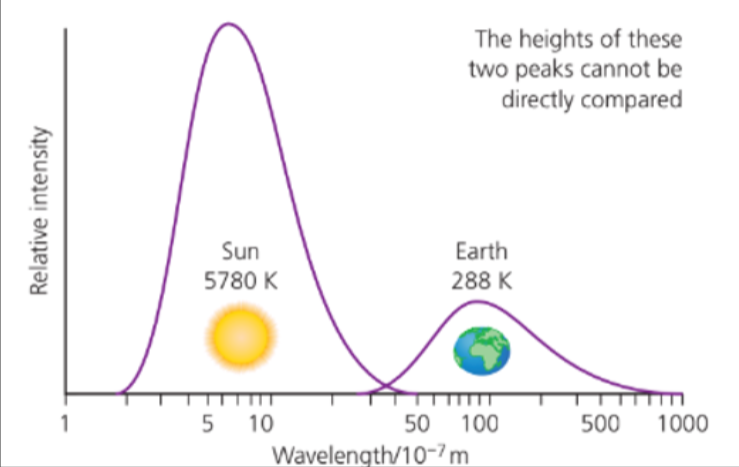
- Compared to the radiation from the Sun, the thermal radiation from the Earth is at a much lower power, with much longer wavelengths.
Greenhouse Gases
- Methane, water vapor, carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide are the main greenhouse gases and each of these has origins that are both natural and created by human activity.
- The chemical formulae for the gases are as follows:
- Methane - CH₄
- Water vapor - H₂O
- Carbon dioxide - CO₂
- Nitrous oxide - N₂O
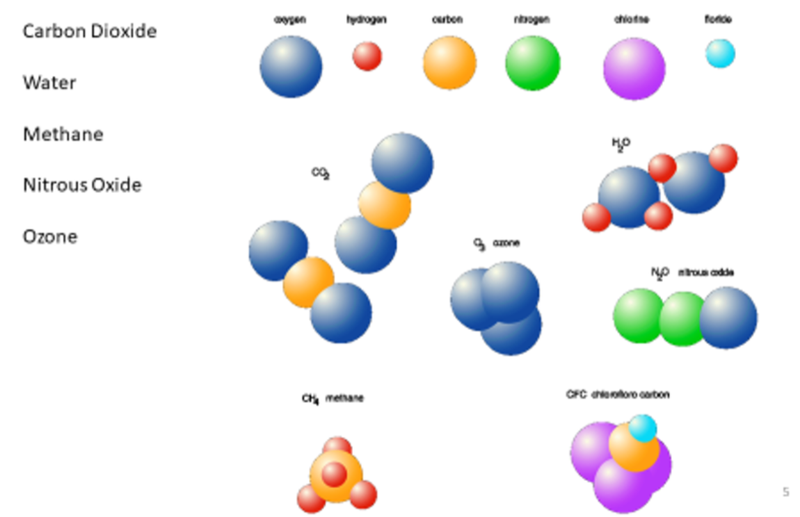
- Molecules of the greenhouse gases absorb some of the thermal (infrared) radiation emitted by the Earth's surface.
- Without these gases, the radiation would continue to travel away from the planet and it would be far colder.
- The molecules will re-radiate the same energy a short time later, but in random directions, which means about half of it is directed back towards the Earth's surface.
- This means that the Earth is significantly warmer than it would be without greenhouse gases.
- If the atoms in a molecule vibrate at the same frequency as the infrared radiation passing through the greenhouse gas, then energy will be absorbed.
- This is due to the phenomenon of resonance.
- This raises the molecule to a higher energy level.
- The energy is quickly released again as the molecule returns to its lower energy level, but the released energy is radiated back in random directions.
- We've seen that the Earth emits much longer wavelengths than the Sun.
- Since most of the radiation from the sun is at higher frequencies it is much less likely to be absorbed than the mostly lower frequencies emitted from the cooler surface of the Earth.
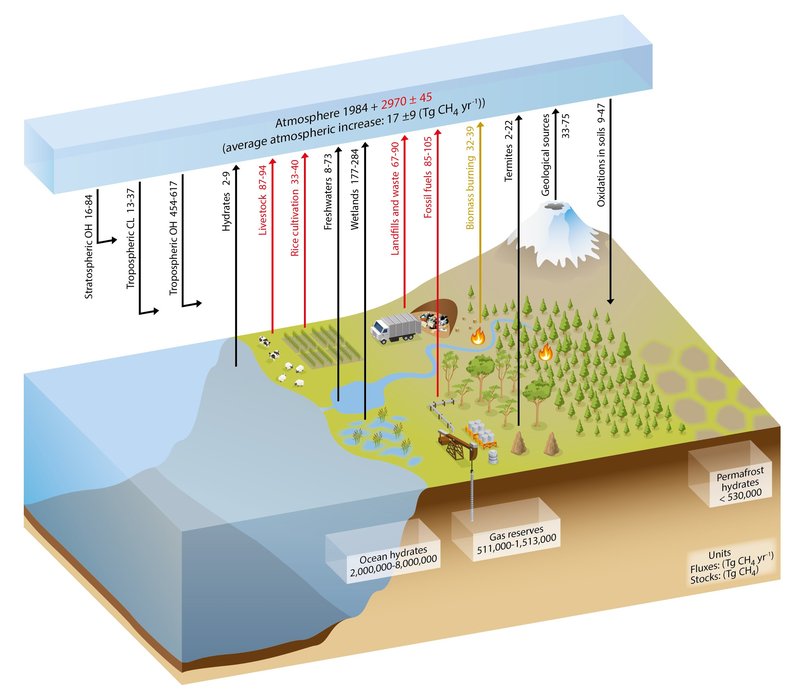
The Carbon Cycle
- As greenhouse gases are always being produced, they need to be absorbed somewhere to prevent the Earth from heating up more and more.
- This is where the carbon cycle comes in.
- There are sources of carbon, such as decaying organisms and waste.
- Carbon sinks, such as plants and the ocean, absorb greenhouse gases like CO₂.
- However, human activity has led to increased greenhouse gases entering the system, more than the carbon sinks can normally absorb, causing an imbalance.
Sources
https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/wg1/carbon-and-other-biogeochemical-cycles/methane_test-3/