What are Normal Forces?
- We've learned about Newton's third law, which states that every force on an object is met with an equal and opposite one.
- Normal force, Fₙ, is the component of this reactive force acting perpendicularly to the surface that counteracts the body applying a force to it.
- Normal force occurs whenever two objects in contact push against each other.
- It is always the reaction to another force.
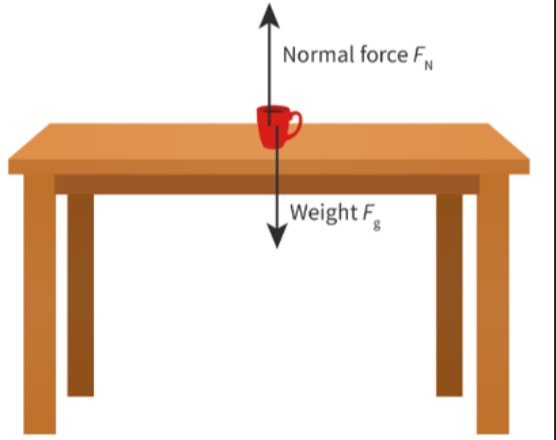
- If an object is standing still on a surface, it means that the normal force pushing the object up is the same as the weight pulling it down.
- However, when the two forces aren't at the same angle, then for the resultant force to be equal, the components of the forces must cancel out.
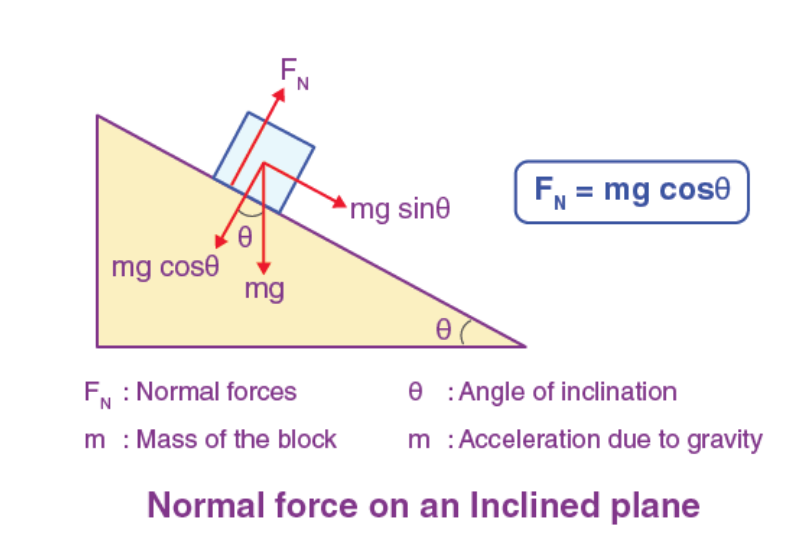
- In the example above, a block is resting on a slope of angle θ.
- As the normal force is perpendicular to the slope, it is not aligned with the gravitational force pulling the block down.
- To determine whether the block actually slides down, we need to decompose the vectors into their horizontal and vertical components!
- By decomposing the vector for weight, we find that mgcosθ must be equal to the negative of the normal force as the slope is holding up the block.
- This means the normal force and mgcosθ cancel out, leaving only mgsinθ.
- As the resultant force is mgsinθ, the block starts to accelerate as it slides down the slope!
Sources