Motion of Charged Particles in Uniform vs Non-Uniform Electric Fields
- The force of a charged particle in an electric field is determined as:
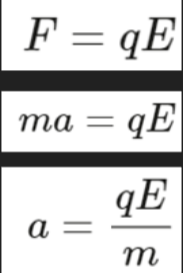
- This formula is obtained from reversing the formula for electric field strength, E, which is electrostatic force divided by charge.
- This is also the formula that was equated to the acceleration due to gravity in Millikan's oil drop experiment!
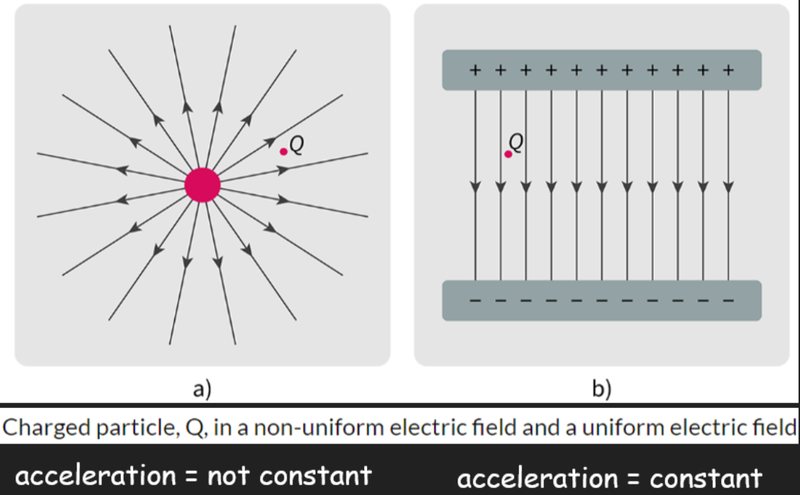
- In a non-uniform electric field, a charged particle's acceleration is not constant.
- This is because the electric field strength is constantly changing with it's separation from the source of the field.
- However, in a uniform electric field, the electric field strength is uniform, meaning it is the same throughout the field.
- This means that the acceleration of a charged particle in a uniform electric field is constant.
Stationary Charged Particles in a Uniform Electric Field
- "Stationary" mobile charges will accelerate along a field line in a uniform electric field.
- This means they will move towards either plate.
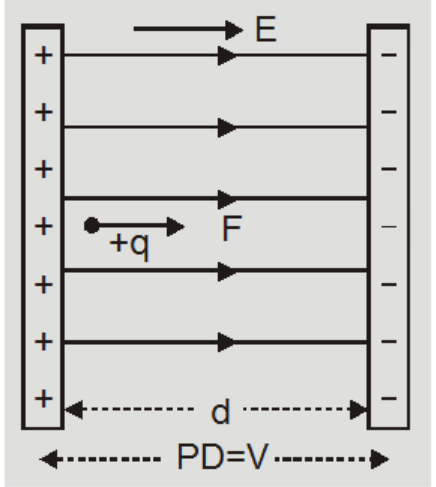
- Likewise, a negative charge would move towards the positive plate.
- Because acceleration is constant, SUVAT equations can be used to determine how the charge moves.
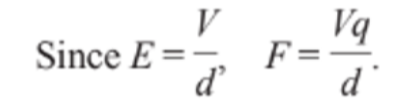
Charged Particles Moving Across a Uniform Electric Field
- We've discussed how acceleration is constant towards either plate depending on the field.
- This is similar to the gravitational acceleration of free fall, which is constant and causes objects to move towards the ground.
- The motion of a charged particle in a uniform field should be similar to that of projectile motion!
- The speed of the particle can be separated from the perpendicular acceleration due to the field.
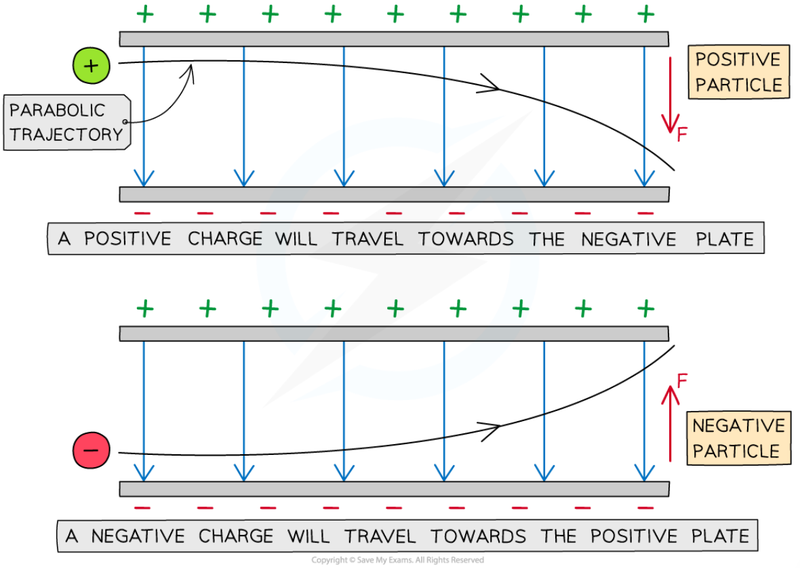
- As a particle moves through a uniform field, it will deflect towards either plate.
- The amount of deflection depends on the mass, charge and speed of the particles.
- Particles of greater mass will need more force to be moved.
- Particles of greater charge will be more susceptible to movement as they experience greater electrostatic force.
- Particles of greater speed will spend less time in the field, and thus be under the effect of the field for a smaller duration.
- Keep in mind that an uncharged particle such as a neutron experiences no force in an electric field and will therefore travel straight through the plates undeflected.
Particle Beams
- Experiments with charged particles will involve a large numbers of particles moving together with the same velocity as a particle beam.
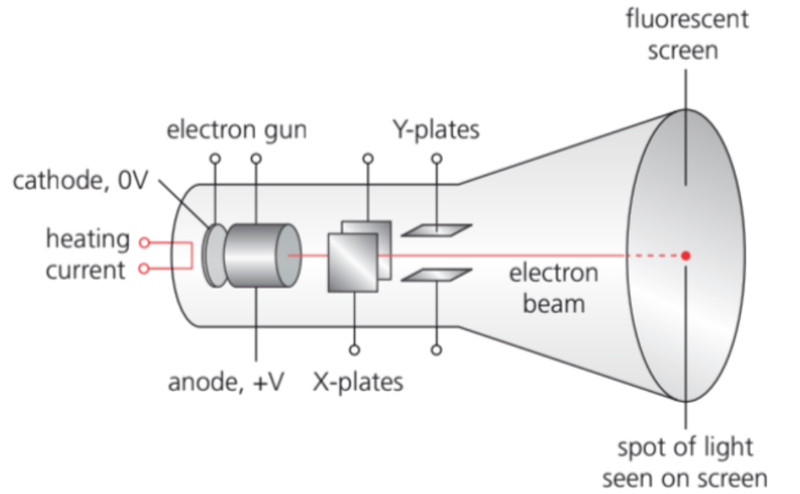
- In the above particle emitter, electrons are shot out of an electron gun to create an electron beam.
- If a potential difference is connected across the X plates, then the particle is deflected either to the right or to the left.
- If a potential difference is connected across the Y plates, the beam is deflected up or down.
Sources
https://www.esaral.com/motion-of-charged-particle-in-electric-field/