What is Friction?
- Friction is a difficulty in movement caused by imperfections in surfaces.
- If surfaces were perfectly smooth, then there would be no friction and everything would go sliding forever (ignoring air resistance) at the slightest nudge.
- Friction and similar forces are all contact forces.
- This means that they can only take affect if two objects are touching one another.
Normal Force and Friction
- Before we discussed how normal force is the force that acts directly perpendicular to an object on a surface.
- While this leads to the weight and normal force cancelling out when an object is placed on a horizontal surface, when it is placed on an slope, there resultant force on the object is mgsinθ.
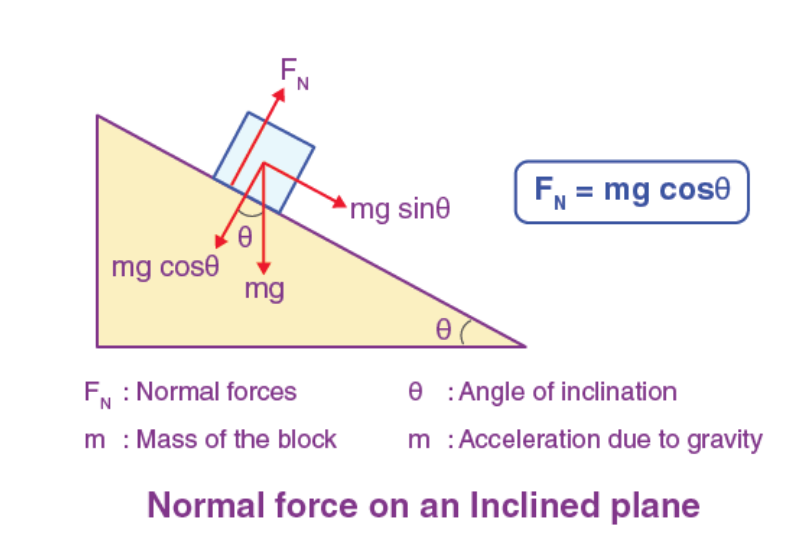
- This would lead to the object accelerating downwards as it slips down the slope.
- Yet, if we test this by putting an eraser on a book, and start tilting it, the eraser does not slip immediately.
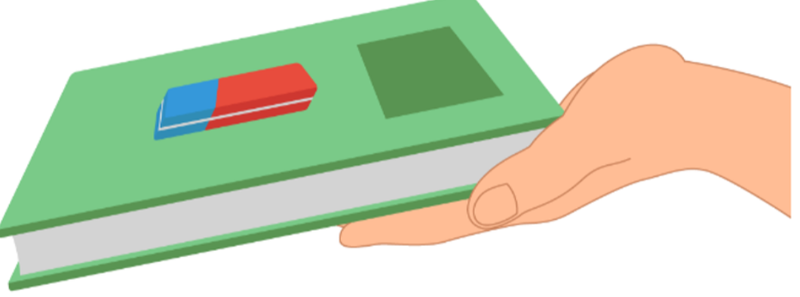
- The reason for this, is that the component of weight, mgsinθ is cancelled out by the friction force, resulting in a net force of zero!
Frictional Force
- Frictional force always acts against movement.
- For example if you are pushing a box, the frictional force will be acting opposite to the direction you are pushing it.
- There are two forms of frictional force, static and dynamic.
- Static frictional force prevents still objects from moving.
- Dynamic frictional force slows down moving objects.
- Static friction is always stronger than dynamic friction, which is why its easier to keep an object moving than to make it start moving.
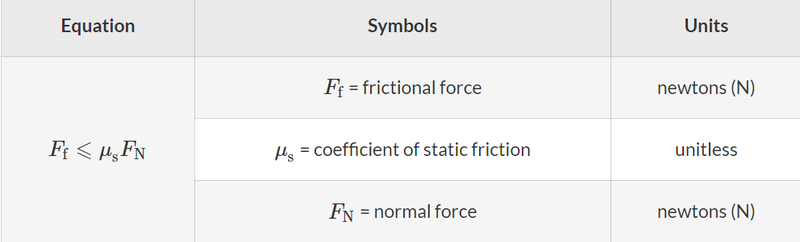
- Frictional force for static friction can be calculated via:
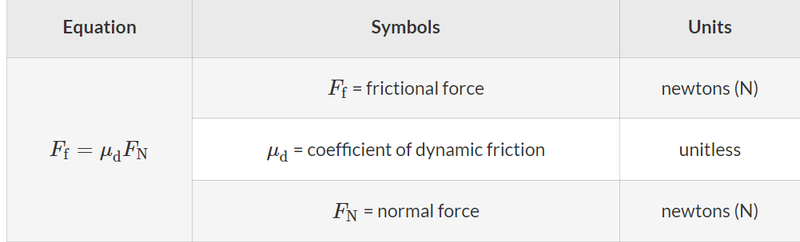
- Frictional force for dynamic friction can be calculated via:
- From these formulae we can see that frictional force is based on the normal force, and the coefficient of friction.
- The frictional coefficient is determined by the roughness of the surface.
- For example ice has a much lower frictional coefficient than asphalt, which is why you can so easily slide across ice: the frictional force resisting your movement is much lower.
- As the normal force is the reactionary force applied against an object applying a force on a surface, the more an object pushes down on a surface, the higher the normal force must be in return.
- For example, try pushing a book across a table. It's probably quite easy.
- However, now try stacking multiple books and pushing them across the table. It'll likely be quite a bit harder.
- The weight of the stack is much more than the single book, and thus the same is true for their normal forces.
Frictional Force in Motion
- Frictional force is the force required to move the object, or keep it moving in the case of dynamic friction.
- The dynamic frictional force is quite simple, as it remains constant as long as the surfaces (which affects coefficient of dynamic friction) and the weight of the object (which affects the normal force) stay the same.
- However, static friction is more tricky.
- Imagine a still box with a rope attached.
- Lightly tugging on the rope doesn't make the box move. After tugging a little harder the box is still not moving. Yet after tugging just a bit harder, the box starts to move.
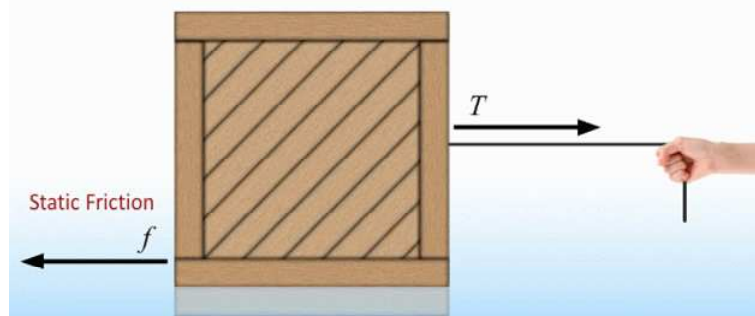
- According to Newton's first law, when the box isn't moving, the resultant force on it must be zero.
- Yet the resultant force shouldn't be zero, as we were tugging on it with a rope. That's where friction comes in!
- If resultant force on an object is already zero, then frictional force is also zero.
- However, when a force tries to move an object, then friction force applies.
- As we tug harder on the rope, the frictional force on the box increases.
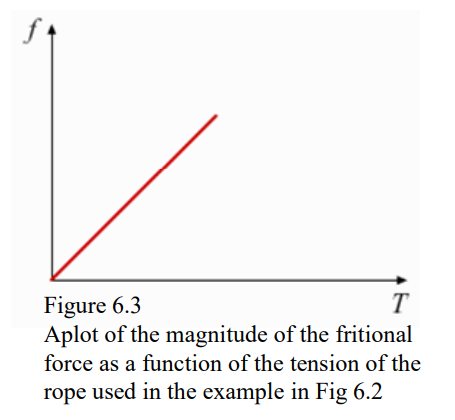
- However, eventually the friction force gives way, and switches from static to dynamic friction, and we can start moving the box, as the dynamic frictional force is less than the static frictional force, while our tension force pulling the box remains the same.
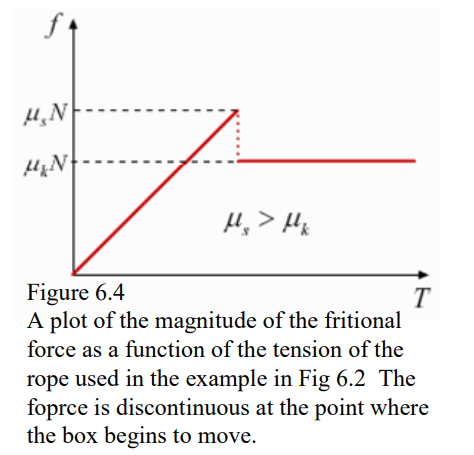
- As the static friction force increases with how much force we pull the rope with, then it must always be less or equal to the maximum possible friction force.
- As we tug harder and harder, frictional force F increases.
- Right before motion begins:
F = Fₘₐₓ = μₛFₙ
- Then the switch from static to dynamic occurs and the object accelerates a little.
- If the applied force is the same as the dynamic friction, then the box will keep moving at the same velocity.
- However, it will start accelerating if we pull with a force greater than the dynamic frictional force.
Sources
https://courses.physics.illinois.edu/phys211/su2012/Text/ch06.pdf