What are Field Forces?
- Field forces are forces that act on objects from a distance.
- This means that they can affect bodies without being in contact.
- You might not feel it, but you're under the affect of field forces all the time!
- The area in which the body is able to alter other objects is called a field.
- Within this field the field forces of an object have an effect.
- While fields are technically infinite in size, the strength of the force in fields diminishes exponentially as you get farther away from the object, eventually making it negligible.
Types of Field Forces
Gravitational Force
- Ever wondered why you can only jump so high but in space astronauts seem to be able to float around freely?
- This is because the Earth's gravitational field is constantly pulling you in, but not the astronauts as they are much farther away from the Earth.
- Gravitational fields are a feature of every single object with a mass - that includes you!
- The larger the mass, the larger and more powerful the gravitational field.
- That's how our sun manages to keep the entire solar system in its orbit.
- If it weren't for the sun, all the planets in our solar system would simply fly away.
- The formula for gravitational force is F = mg.
- In this case g stands for the acceleration of free fall, which is 9.8 m/s² on Earth. However keep in mind that this value is different on different planets.
- Weight is used to notate the gravitational force that bodies experience. For example, even if your mass is the same, your weight would be much less on the moon, and nonexistent in a vacuum.
Free Fall
- When a body is dropped near the surface of the Earth, it falls downwards. This motion is called free fall and it is uniformly accelerated motion.
- The constant for free fall is 9.81 m/s².
- Bodies accelerate in constant motion in free fall.
- The mass of objects is not important in free fall, no matter the weight, all objects fall at the same rate.
- Generally when calculating free fall, air resistance is ignored.
- When air resistance is accounted for, mass affects free fall significantly.
Electromagnetic Force
- Electric charge is a property of matter and depends on the matter’s microscopic structure.
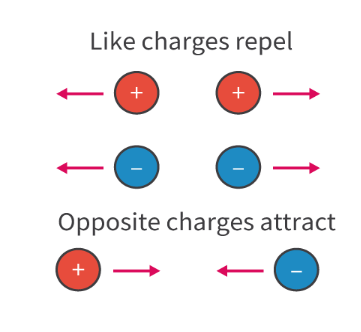
- There are two types of charge: positive charge (+) and negative charge (−).
- Electric charge occurs due to electrons in atoms.
- Objects with similar charges repel and those with different charges attract.
- Magnetic forces occur for the same reason.
- Charged particles all have electric fields, when these fields align they can create powerful magnetic fields.
- Like electric forces, different magnetic charges attract and the same charges repel.
- Some materials can be easily magnetized whereas others aren't magnetic. For example most metals are magnetic and thus can be magnetized by being put in an electric field.
- The Earth itself has its own magnetic field as well!
Nuclear Forces
- Nuclear forces are the forces that act between two or more nucleons.
- Nuclear forces bond protons and neutrons.
- They are very strong forces, which is why splitting atoms releases so much energy!
