LeFonch
Enhanced Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
Why Does Global Warming Occur?
- Global warming, or global heating, is attributed to the enhanced greenhouse effect.
- This is caused by the increased concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides act like a blanket and trap heat inside the Earth's atmosphere.
- As concentrations of these gases build up, they are more effective at preventing heat being lost into space.
- The amount of heat being lost from the atmosphere is less than the energy entering the atmosphere.
- As a result the temperature of the atmosphere increases.
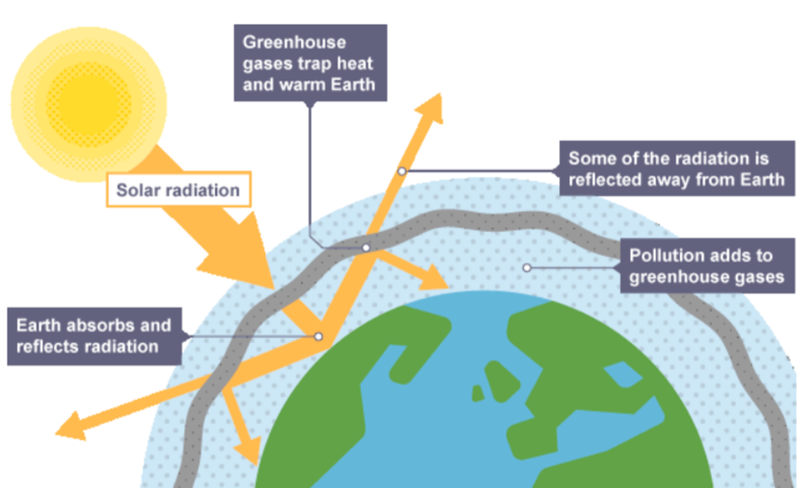
Enhanced Greenhouse Effect vs Normal Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse Effect
- Solar radiation passes through the Earth's atmosphere.
- The Earth absorbs most of the radiation and warms up.
- The Earth radiates heat energy.
- Some heat escapes into space.
- Some heat is absorbed by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Greenhouse gases radiate heat in all directions.
- The lower atmosphere remains warm.
Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
- Greenhouse gases allow more solar radiation to pass through the Earth's atmosphere.
- The Earth absorbs most of the radiation and warms up.
- The Earth radiates heat energy.
- Less heat escapes into space.
- More heat is absorbed by the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Greenhouse gases radiate heat in all directions.
- The lower atmosphere heats up.
Consequences of the Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
- Increasing temperatures of the oceans, land and atmosphere, disrupting ecosystems.
- Climate change, melting snow and ice.
- More frequent extreme weather conditions such as hurricanes, storms, floods, droughts and fires.
- Rising sea levels.
- Increased acidity in the ocean as it absorbs more greenhouse gases.
Wien's Law and the Greenhouse Effect

- The peak wavelength of radiation emitted from the Earth can be calculated using Wien's law.
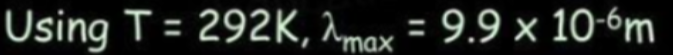
- This wavelength is in the infrared region.
- Infrared radiation is absorbed by the main greenhouse gases in the atmosphere which re-radiate the energy back into the Earth.