What is Electric Charge?
- All atoms are made up of protons, neutrons and electrons.
- While neutrons are neutral, protons have positive charge, and electrons have negative charge.
- Protons and neutrons are stuck together in the nucleus, but electrons are free to move around.
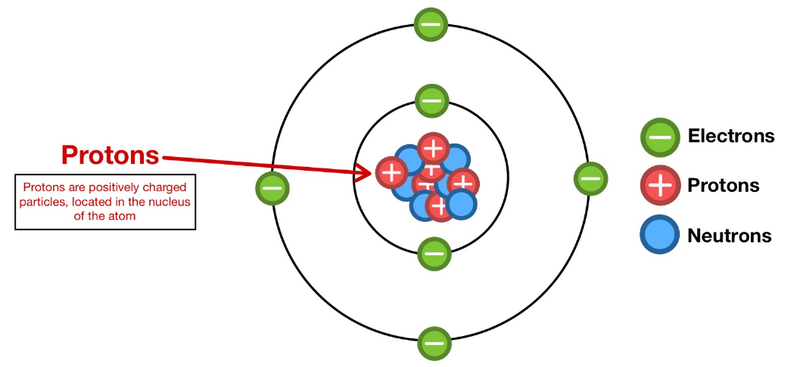
- Normally the protons and electrons of an atom balance each other out, leading to a neutral total charge.
- However, if the electrons move away from an atom, then it has positive charge, as it now has more protons than electrons.
- If more electrons come to an atom, then it has negative charge, as it has more electrons than protons.
- Like charges repel one another, which means that two positive charges or two negative charges will push each other away.
- Opposite charges attract one another, which means that a positive and a negative charge will pull each other.
Measuring Charge
- Electric charge is measured in coulombs, written as C.
- One electron has a charge of -1.6 * 10⁻¹⁹ C.
- Likewise one proton has a charge of 1.6 * 10⁻¹⁹ C.
- Any charge of an object, q, is equal to a specific amount of electrons, as electrons are the smallest possible unit of charge.
q = Ne
- Where N is an integer number, q is the charge of the body, and e the charge of an electron.
- The total charge in an isolated system remains constant.
Electrostatic Charging and Discharging
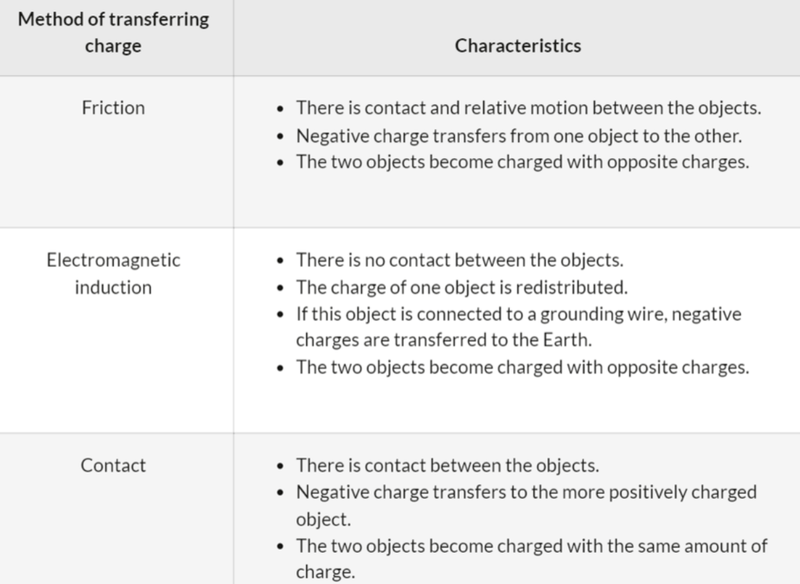
- Electric charge can be transferred between bodies using friction, electrostatic induction and by contact.
Charging by Friction
- When friction occurs between substances, electrons are often transferred between their surfaces.
- When objects come in contact with each other, excess electrons or a deficit of electrons may be shared between them.
- This is why you sometimes get shocked if you touch a doorknob!
- The electrons in your hand are transferred to the doorknob.
Charging and Discharging by Contact
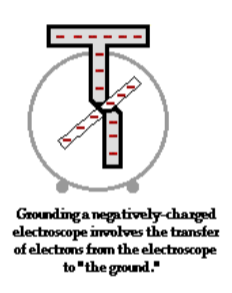
- Charged objects will become discharged if they are connected to the ground.
- If this is done deliberately, it will happen very quickly and it is called grounding or earthing.
- The object will then have zero charge.

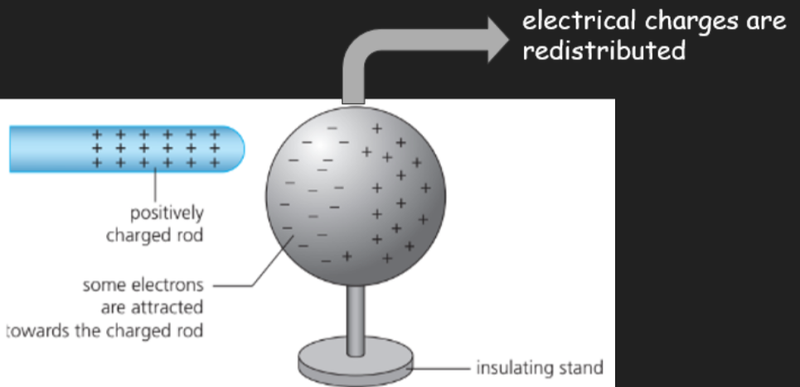
Charging by Electrostatic Induction
- Electrostatic induction is the movement of charged particles (electrons) caused by the influence of a nearby charged object, but without physical contact.
Characteristics of Methods of Transferring Charge
Sources
https://ar.inspiredpencil.com/pictures-2023/protons-neutrons-electrons-charges