What is Coulomb's Law?
- Like gravity, electrostatic force is one of the four fundamental forces.
- The force between two charged particles is given by Coulomb's law, created by French engineer and physicist Charles Coulomb.
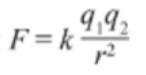
- Where q represents the charges of the objects the distance between them, and k represents the Coulomb constant.

- This law should seem familiar, because it is arranged the same way as Newton's law of gravitation!
- Gravitational force is replaced by electrostatic force.
- Masses are replaced with charge.
- And the gravitational constant is replaced with Coulomb's constant.
Permittivity
- Coulomb's constant k is based on the permittivity of free space.
- The electrical permittivity of free space ε₀ is a fundamental constant that represents the ability of free space to transfer an electric force and field.
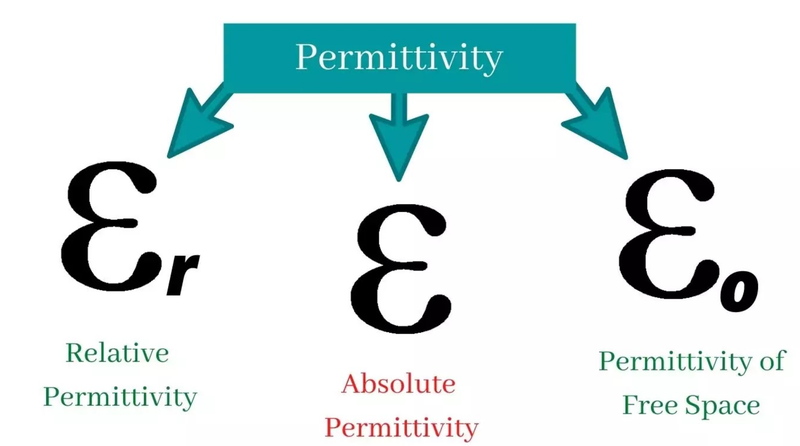
- Likewise, the absolute permittivity for other substances is based on their ability to transfer an electric force and field.
- The relative permittivity is calculated as a ratio:

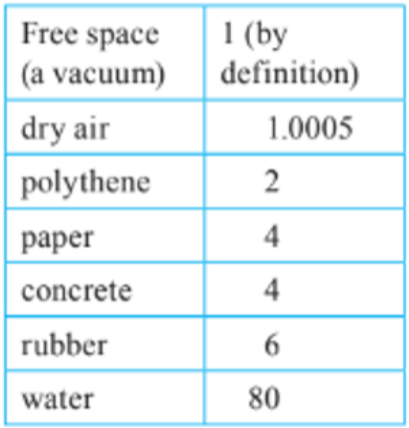
- As you can see in the chart, more conductive materials have a higher level of permittivity.
- In most cases the permittivity of air is assumed to be the same as that of free space.
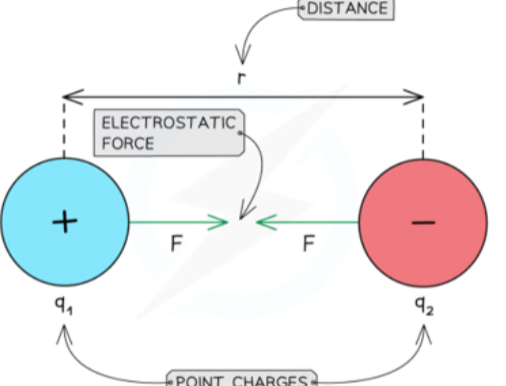
Repulsive and Attractive Forces
- Unlike gravitational force between two masses, which is only attractive, electric forces can be attractive or repulsive.
- This is because charge can be positive or negative, unlike mass, which is only positive.
- Between two positive or two negative charges:

- Between a positive and a negative charge:
Sources
https://www.electricity-magnetism.org/electrostatics/coulombs-law/
https://www.atlearner.com/2022/04/permittivity-of-free-space.html#google_vignette