Alpha Decay
- The composition of an alpha particle is the same as a helium-4 nucleus.
- It is the combination of two protons and two neutrons, which is very stable.
- It has a nucleon number of 4 and a proton number of +2.
- Alpha particles can be represented by the symbols:
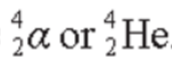
- The radioactive decay equation is a balanced nuclear equation which shows a radionuclide and its decay products.
- It is in the form of:
- parent nucleus -> daughter nucleus + alpha particle
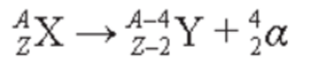
- As an example, the decay of radium-226 results in the emission of an alpha particle:
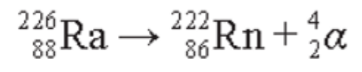
- Alpha particles have considerable kinetic energy.
- However, they have limited penetration of matter (penetrating power).
- This is because they transfer significant amounts of energy in collisions with other atoms/molecules.
- The collisions transfer the energy needed to ionize a large number of atoms/molecules in the material through which the alpha particles are passing.
- After most of their energy has been transferred, the alpha particles are effectively absorbed as tiny amounts of helium.
Beta-Minus Decay
- In an unstable nucleus it is possible for an uncharged neutron to be converted into a positive proton and a negative electron.
- This also involves the creation of another particle called an antineutrino.
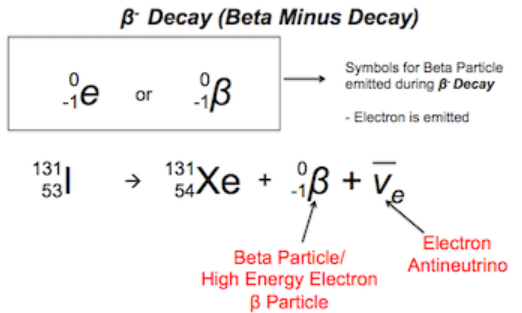
- The emitted electron is called the beta-negative particle.
- When beta-negative, or beta-minus, decay occurs, the number of nucleons in a nucleus remain the same, but the number of protons increases by one, so that a new element is formed.
- This can be represented in a radioactive decay equation of the general form:
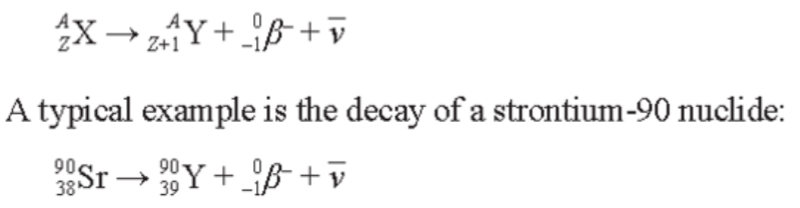
- Antineutrinos (and neutrinos) are very small particles with no charge, which travel at speeds close to the speed of light, so they are very penetrating and very difficult to detect.
- An antineutrino is an antiparticle, which is a particle with the exact opposite physical properties of another.
- It is the antiparticle of a neutrino.
- Antimatter is matter consisting of antiparticles such as neutrinos.
- When a particle and its antiparticle interact they annihilate each other, and all their mass is converted into electromagnetic energy.
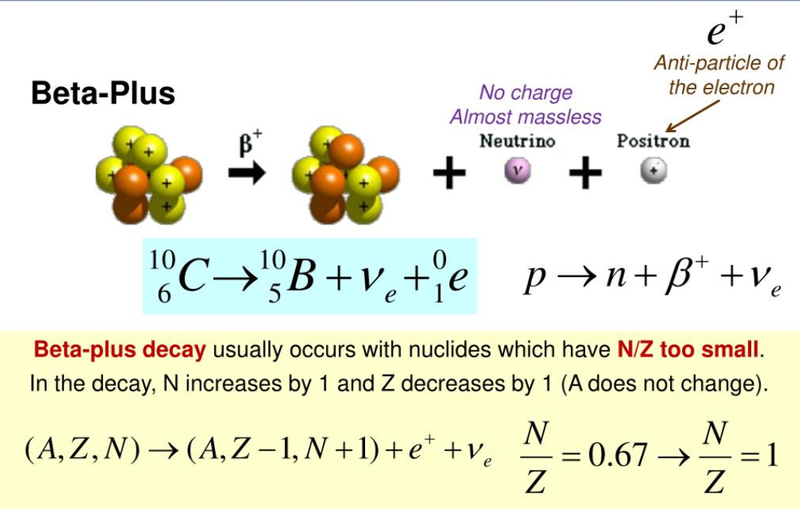
Beta-Plus Decay
- In a similar process to beta-negative decay, called beta-positive or beta-plus decay, a proton in a nucleus can be converted into a neutron and a positively charged electron, called a positron (another example of antimatter), which is then ejected from the atom, after which it is called the beta-positive particle and is represented by the symbol of:
- The positron is an antiparticle of an electron.
Beta-Plus Decay vs Beta-Minus Decay
- Beta-minus decay is radioactive decay resulting in the emission of an electron and an antineutrino.
- A neutron is converted into a proton and an electron.
- In beta-plus decay there is radioactive decay resulting in the emission of a positron and a neutrino.
- A proton is converted into a neutron.
- In both decays the nucleon number stays the same but the number of protons changes.
Developing Neutrinos
- Consider alpha and beta-minus decay again:
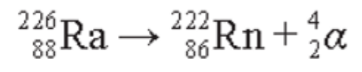
- The alpha particles from these decays always have discrete amounts of kinetic energy.
- However, the beta particles were found to have a continuous range of kinetic energies.
- This would mean that mass/energy wasn't being conserved.
- However, the beta particles were found to have a continuous range of kinetic energies.
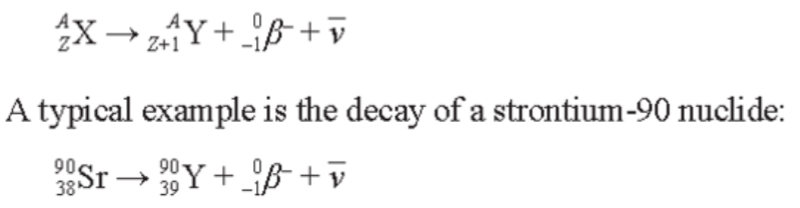
- The answer is that some other particles must be produced as well.
- This leads to the description of the neutrino and antineutrino.
- The energy of the neutrino/antineutrino varies as they are emitted in random directions.
- This is what allows a range of energies while maintaining mass/energy conservation.

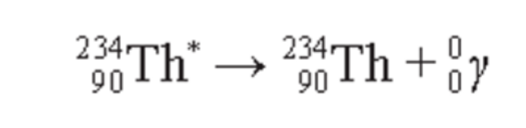
Gamma Decay
- Gamma rays are high-frequency electromagnetic radiation (photons) released from unstable nuclei.
- A typical wavelength is about 10^-12m.
- This corresponds tot he energy of about 1MeV (using E = hc/λ).
- Gamma rays are usually emitted after an unstable nucleus has emitted an alpha or beta particle.
- Gamma rays are represented by the symbol γ, gamma.
- Gamma radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted from some radionuclides and it has an extremely short wavelength.
Blocking Radiation
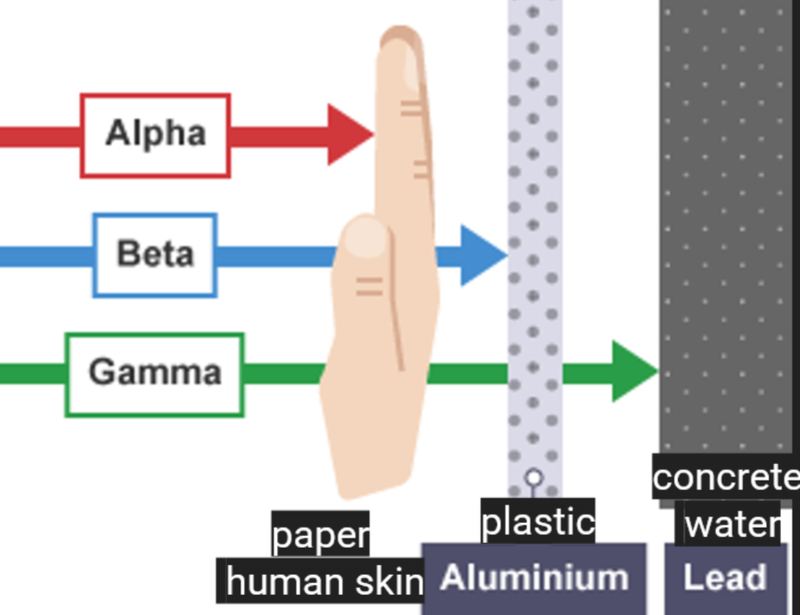
- Alpha particle radiation is the least penetrative, while gamma radiation is very penetrative.
Summary of Particles

Deflection of Nuclear Radiation in Electric and Magnetic Fields
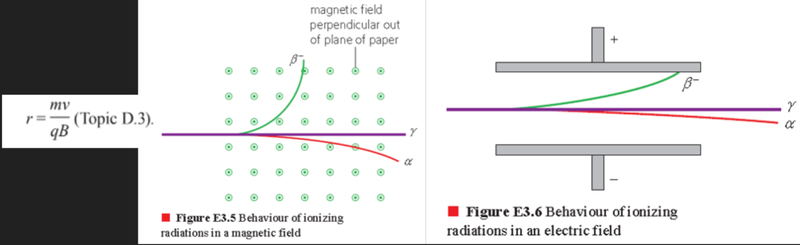
- Alpha and beta radiation will be emitted in random directions from their sources, but they can be formed into narrow beams by passing the radiation through slits.
- This process is called collimation.
- Because a beam off alpha particles, or beta particles, is a flow of charge, they will be deflected if they pass across an electric or magnetic field.
- Gamma rays carry no charge and are thus unaffected.
Decay Series
- A radioactive decay does not always produce a stable daughter nuclide.
- If the daughter nuclide is unstable, it will also decay.
- In some cases, there is a series of decays, called a decay series, that does not end until a stable nuclide is reached.

Sources
https://study.com/academy/lesson/radioactive-decay-definition-formula-types.html