What is the Sine Rule?
- The sine rule shows that the ratio of the size of an side and the sine value of its opposite angle in a triangle are equal to all the other ratios in a triangle.
- Just like the cosine rule, it is applicable to all types of triangles.
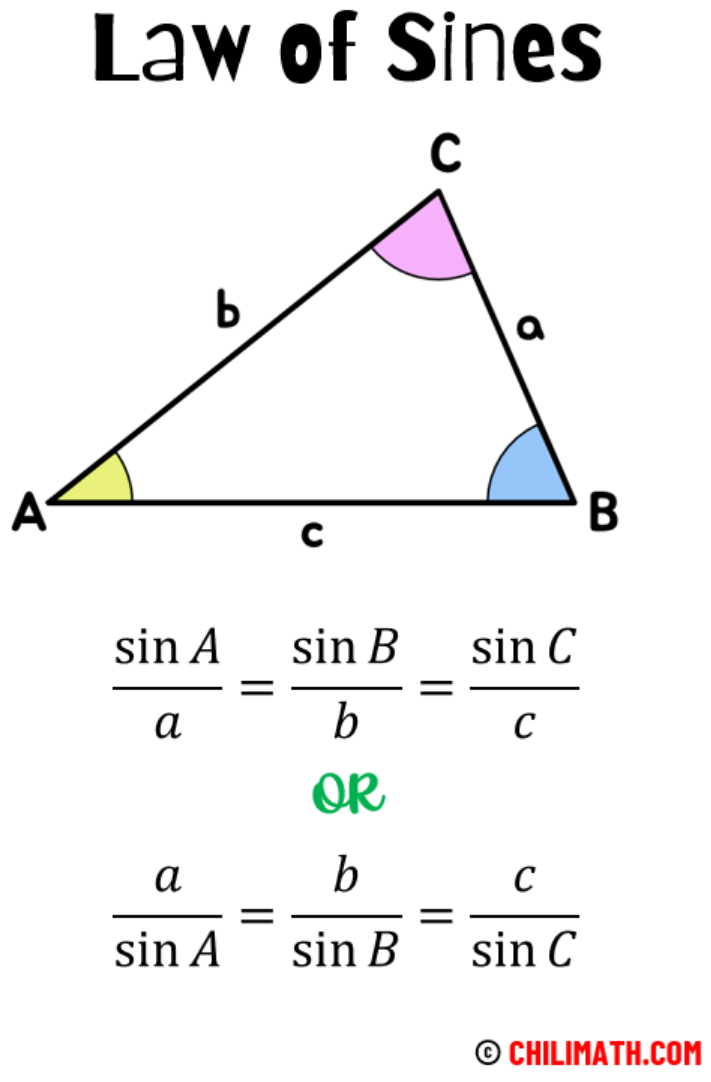
- The sine rule is used to solve triangle problems when there are two given angles and the length of one side of a triangle to find the missing lengths.
- Given the length of two sides and an angle not included between the two sides to find the missing side and angles.
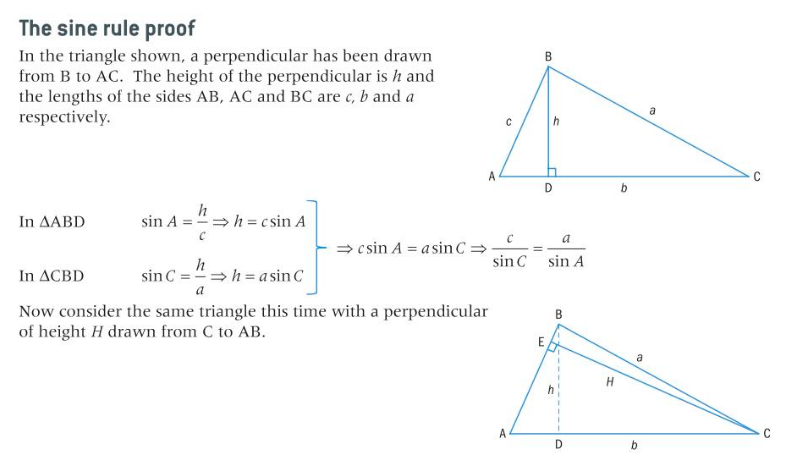
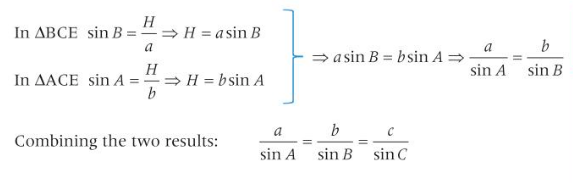
Sine Rule Proof
The Ambiguous Case of the Sine Rule
- The ambiguous case of the sine rule occurs when two triangles can be constructed from given information about two sides and the non-included angle in a triangle.
- Given the length of sides b and a as well as angle A, two triangles can be constructed.
- The angles B are supplementary.
- This means that 180° - B₁ = B and vice versa.
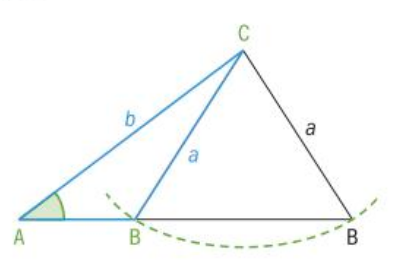
- To determine whether the ambiguous case of the sine rule experiment with the shape of the triangle to see whether it is possible to construct a second triangle.
- Generally very narrow triangles that slope to one side or triangles that look like "cheese wedges" are applicable.
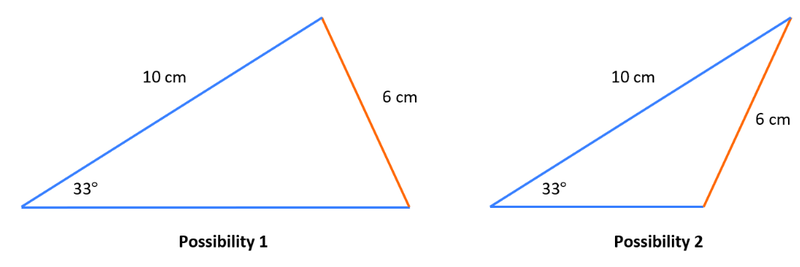
- In an exam, a question might hint to the existence of an ambiguous sine rule, such as if it asks "Find the values...".
Sources
https://www.chilimath.com/lessons/trigonometry/law-of-sines/
https://www.wizeprep.com/textbooks/high-school/mathematics/19600/sections/2555140