Long Division
- Long division is a method of dividing numbers, and is especially useful when it comes to big numbers and polynomials.
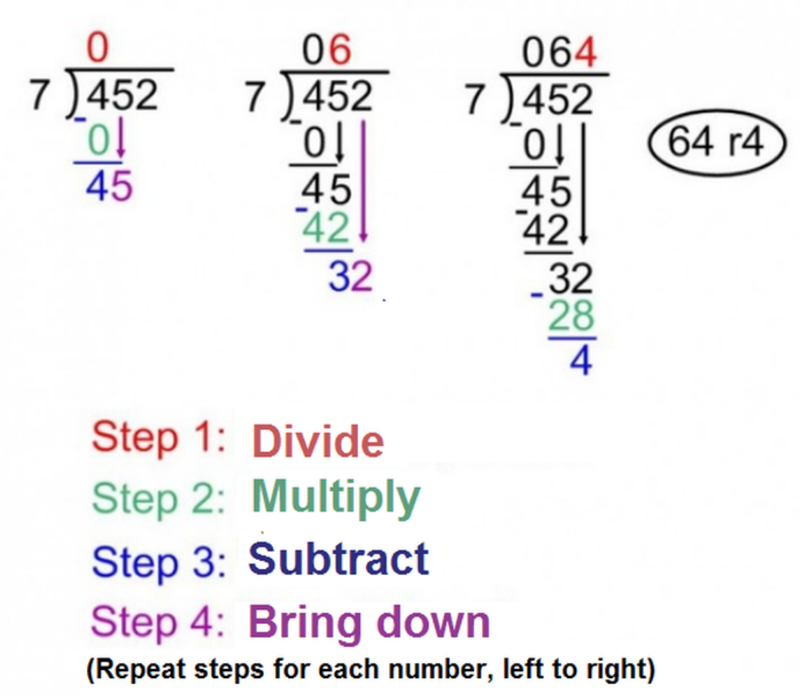
- You arrange the denominator on the left, and the numerator to the right.
- Check how many times the denominator can fit into each of the terms of the numerator, and write the amount on the top.
- Add the difference between the amount of times the numerator fits in the term and the term itself below.
- Then bring the next term down, and repeat the process.
- This should ideally continue until the difference between the amount of times the numerator fits in the term and the term itself is zero.
- If there is a difference left that cannot be divided, then that is the remainder.

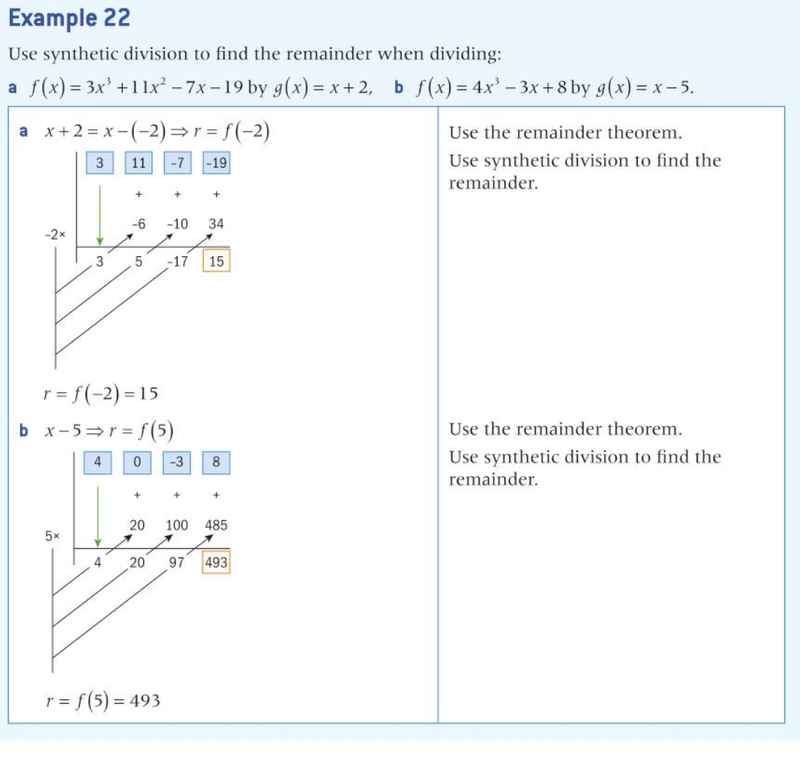
Synthetic Division
- Synthetic division is a far quicker way to do long divison.
- Yet it has a catch! It only works if the denominator is a linear function.
- Long division works all the time, even if the denominator is a polynomial too.
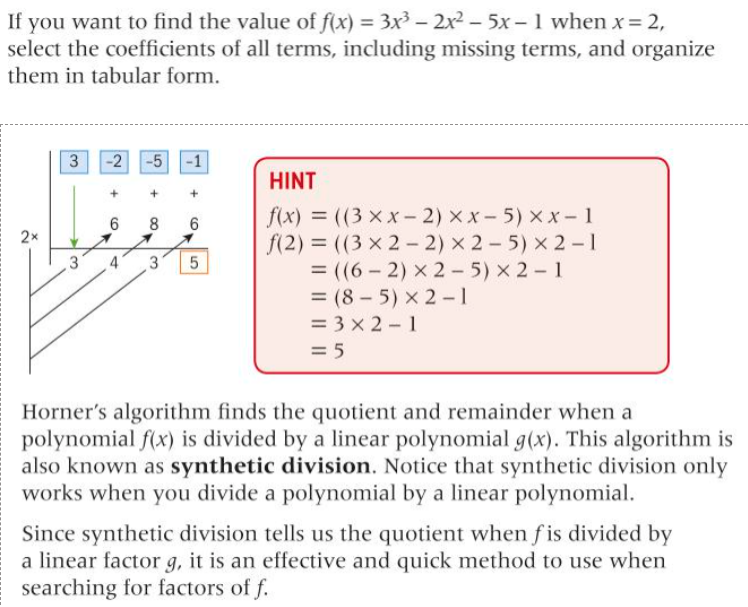
- It uses the zero of the linear function on the left side.
- The multiplier of all the values of the numerator are placed at the top.
- Each one is subtracted by the zero multiplied by the previous multiplier brought down, and is then brought down itself.
Sources