The Fall of the Western Roman Empire
- The Western Roman Empire controlled most of Europe at the time.
- The empire was mainly led by a central government with provinces being led by local governments.
- When the Western Roman Empire collapsed in 476, the government and economy collapsed, having a great effect on Europe.
- The collapse of the empire led to the start of the Middle Ages.
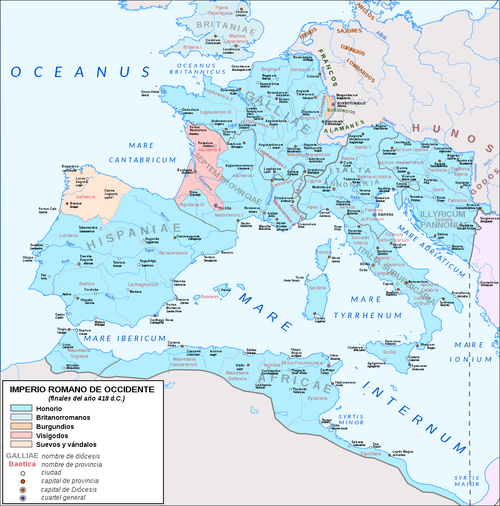
- A map of the Western Roman Empire.
The Middle Ages
- The Middle Ages (or the Medieval times, or Dark Ages) was a period of time roughly from the year 500 to 1500.
- This era is signified by poor quality of life and generally lacking technology as a lot of information had been lost from the Western Roman Empire.
Feudal Society
- After the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, societies in the Middle Ages became very scattered.
- Feudal societies were the most common throughout Europe, where the land would be owned by a king.
- This led to there being many kingdoms and empires instead of the countries we know today.
- In feudal societies there was a very strict class hierarcy.
- Kings would be the most powerful in the state. Kingship would be inherited.
- Kings would give out their land to lords such as clergy and nobles who would be loyal to the king and manage the land.
- Similarly knights would be vassals to the lords and would be given protection, food and shelter in order for military service.
- Peasants and serfs who worked on the land would be given protection and shelter. They would pay a lot of rent to the higher classes and often lived in harsh conditions. Peasants and serfs would live on the land in the same conditions for generations.
- Kings and nobles would often have feasts and parties whereas peasants and serfs would barely have enough food to live through the winter.
- Serfs were technically worse-off than peasants, as although both lived in extreme poverty, serfs were effectively slaves, directly owned by the king on whose land they lived on whereas peasants had more freedom. Although peasants were often too poor to move so the difference was very slight.
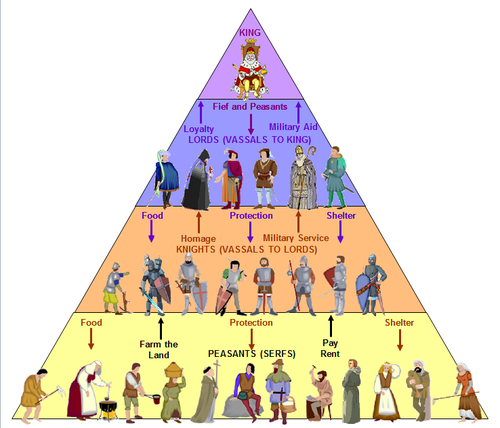
- A chart showing the power hierarchy in feudal societies.
Estate-Based Society
- The feudal system gave birth to this estate-based society.
- An estate-based society didn't allow people to change social classes.
- This meant that people on the lower classes living poor lives could never improve their conditions no matter how hard they worked. Likewise those living in the higher classes were often born into their prestige.
The Idea of Shared Christendom
- Everyone in Europe during the Middle Ages was a Catholic Christian.
- This generally united people in Europe and reduced prejudice (except against minorities such as Romani people who were often heavily persecuted).
- There were often complications such as multiple popes at one time or conflicts such as the Crusades which were series of conflicts supported by the Christian Latin Church.
The New Age of the 1500s
- Christopher Columbus came across (he hadn't discovered as there were already natives living there) the American continent which would pave the way for European exploitation of the continent.
- This leads to a great increase in merchant trade.
- Kings become more inclined to pay for a military to form armies.
- The importance of nobles and knights decreased because of this.
- The development of firearms and efficient ships allowed for conquest and trade.
- This led to the birth of modern, centrally-led states.
The 17th Century
- The birth of international law.
- The development of countries, technology and society.
The Idea of Sovereign States
- Sovereign states are described by having a permanent population (citizens), its own territory, its government not being under another government's control and the capacity to interact with other sovereign states (negotiate, trade, go to war, etc.).
- The idea of Sovereign states allowed kings to rule over their entire country without the need for nobles.
- Sovereign states had full control over their domestic affairs and territory.
- Democracy wasn't yet adopted so sovereign states were still ruled by a king.
The 19th Century
- After the rise of ideologies such as Nationalism and impactful events such as the Industrial Revolution and the French Revolution estate-based society was crumbling.
- This led to the downfall of the three estates of the realm which were nobles (kings and royal families), clergy and the bourgeoise.
- Of course many nations still persisted as monarchies and such figures all had considerable power, but not the complete control they had as was before.
The Rise of Nationalism
- Nationalism is an ideology where people follow the same cultural ideals as their ruler, such as religion and language.
- Effectively this led to nations or societies being formed of people with the same ethnicities, beliefs and languages.
- People would have their own "nation state".
- However there were of course differences between people but their general beliefs would be similar and they'd be fluent in the national language of the state.
- This ideology often brought similar people close together, but also caused rivalries between different groups.
- Minorities were often persecuted or mistreated due to nationalist beliefs, such as Jews in Europe.
Birth of a Civil Society
- Citizens were given rights and duties.
- People in a nation had developed from subjects to citizens, and were no longer fully controlled by their leaders.
- The rulers had reduced power, and decisions were usually made by a government instead of a single king or noble.
- It could be said that rulers had become leaders.
- Civil societies gave more rights to citizens, such as the ability to vote.
- Voting created a situation where leaders had to follow the choice of the majority vote, instead of their own.
- If a leader were to make brash or stupid decisions, they ran the risk of getting voted out.
Estate-Based System vs Civil Societies
- An estate-based system has a ruler which rules over everyone within their territory. Whereas in a Civil society people had far more rights.
- Rulers would have all the power whereas those being ruled over had no say in any matter or ability to make change. In a civil society voting allowed decisions to be made fairly.
- In a civil society leaders had to follow on the ideas of their citizens, juxtaposed to an estate-based society where rulers could go on a foolish war for glory, bankrupting their nation (or other stupid moves).
The 20th Century
- Nation-states (which were states usually consisting of people of one ethnicity) and international law led to the creation of the international system.
- This system laid the groundwork for the development of society and signs of it are still present today, although it has been considerably changed and is far more in-depth.
- There are now several international organizations that influence countries.
- A few examples would be the UN, EU, the Criminal Courts of Haag, Amnesty, NATO, WHO and so forth.
- Some organizations such as the League of Nations are now defunct (although the United Nations plays the same role).
Image Sources: