The Gini Coefficient
- The measure of the distribution of income within an economy.
- This coefficient is used to determine the level of income inequality.
- A higher Gini coefficient means that there is more unequal the income distribution.
- A Gini coefficient of 1 would mean that only 1 person has all the income in an economy.
- A lower Gini coefficient means that there is more equal income distribution.
- A Gini coefficient of 0 means that everyone in the economy has equal income.
- While the Gini coefficient is often a decimal number between 0 and 1, don't be confused if it is expressed as an index number between 0 and 100 instead.
Lorenz Curve
- The y-axis is the cumulative percentage of income.
- The x-axis is the cumulative percentage of the population.
- The curve modelling full equality, called The Line of Equality, would be a straight line at 45 degrees to either axis.
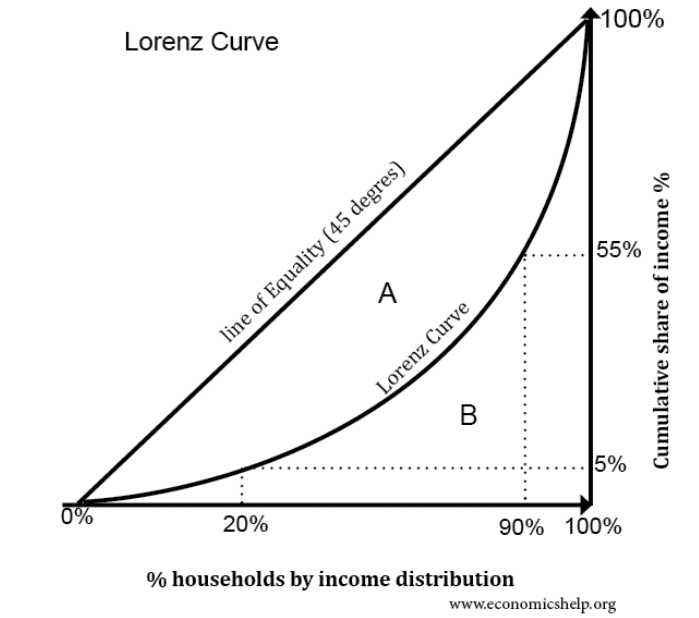
- As the line of full equality can be written as the function y=x, it shows that everyone gets the same income.
- This is because along the line of full equality, the cumulative percentage of income and cumulative percentage of the population increase proportionally.
- However, usually the Lorenz curve is not straight but curved downward.
- The Lorenz curve thus shows the difference between perfect equality of income and the current status of a country's income equality by using the Gini coefficient/index.
- The Gini coefficient is represented by the area between the Lorenz curve and the line of perfect equality.
- Gini coefficient = A/(A+B)
Sources