Free Trade
- No barriers to trade between countries.
- Considered to be the most allocatively efficient system.
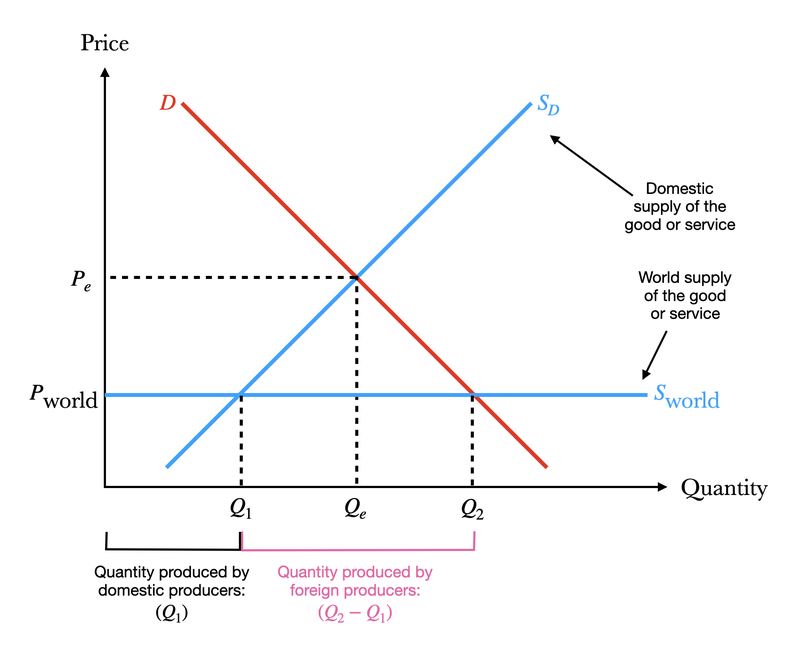
- The free trade market diagram has the price of an item in the y-axis, and the quantity in the x-axis.
- It shows a market for a specific good in a country.
- This is similar to a microeconomics supply-demand diagram.
- The graph shows a domestic situation, where the supply curve shows Domestic Supply and the demand curve is Domestic Demand
- If there is free trade, then there is a third supply curve.
- This is a fully elastic supply curve, which is the World Supply.
- The price at which the world supply meets the y-axis is called the World Price.
- If the world price is lower than the domestic price at equilibrium, then there will be imports.
- This is because foreign firms are more efficient at producing the good than most local firms.
- If the world price is greater than the domestic price at equilibrium, then there will be exports.
- The is because foreign firms are less efficient at producing the good than most local firms.
- If the world price is lower than the domestic price at equilibrium, then there will be imports.
Benefits of Free International Trade
- Increased competition
- Lower prices
- Greater choice
- Aquisition of resources
- More foreign exhange earnings
- Access to larger markets
- Economies of scale
- More efficient resource allocation
- More efficient productions
Increased Competition
- International trade allows for firms in other countries to compete with one another, leading to increased competition and higher quality.
Lower Prices
- Countries are able to specialize and use economies of scale to decrease their costs of production and sell their products at a lower price.
Greater Choice
- Free trade enables domestic consumers to have a greater choice as they are able to select goods and services domestically and internationally.
Acquisition of Resources
- Each country has access to specific natural resources.
- Free trade allows for countries to sell their resources for production in other countries.
Foreign Exchange Earnings
- Foreign exchange earnings refer to financial gains made by currencies exchanging on the global market.
Access to Larger Markets
- Individual firms would have access to a global market instead of being limited to their domestic market.
- Free trade allows companies to become multi-national and gain more consumers.
Economies of Scale
- Larger markets allow firms to gain larger revenue.
- Firms have the option to invest that revenue into increasing efficiency and lowering costs.
More Efficient Resource Allocation
- Free trade allows countries to allocate their resources more efficiently.
- This is because free trade allows countries to specialize in the areas they are best at.
Sources