Purpose of Using UCD Strategies
- For designers to successfully integrate usability into the design process, they require a holistic understanding of how a product, service or system is used.
- Designers must identify user requirements through the use of careful observation and interviews.
- A clear strategy for UCD will improve acceptability and usability, reduce costs and effort and fulfill user requirements.
- When considering strategies for UCD, a variety of techniques need to be considered.
- Most common techniques are field research, method of extremes, observation, questionnaires, affinity diagramming, participatory design and prototype testing.
Field Research
- First hand observation of a customer's user experience.
- As field research is conducted in the user's natural environment, a more realistic view of how the product will be used and how users react to it is obtained.
- Field research can offer first hand knowledge and experience, as well as detailed data of people and processes.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Field research generally emphasizes the relevance of social context.
- However, data from field research can be very narrow and emotional observations might not be genuine due to the relationship between the user and the researcher (has to be developed).
Method of Extremes
- The method of extremes looks at the distribution of a user population. Users are categorized to represent the extremes of a user population, typically the 2.5th and 97.5th percentile.
- Products are then designed and tested to ensure that they function efficiently for those users.
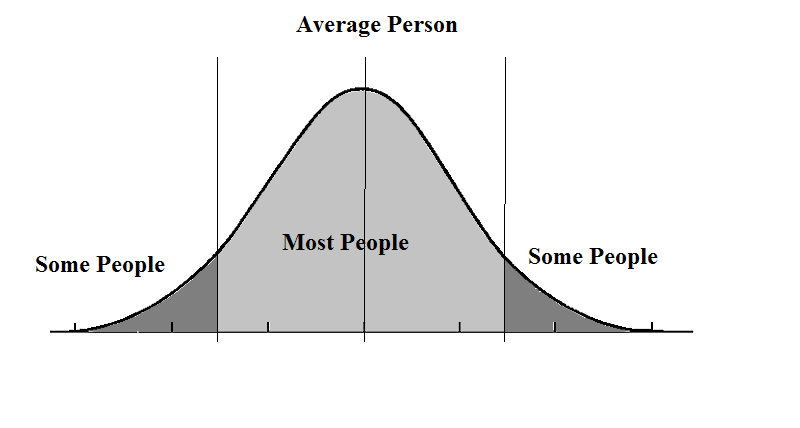
- Distribution of users can be shown on a bell curve. The average population is at the middle, whereas the extremes are to the right and leftmost ends
- The problem with designing for the average user, is that as you move away into the non-average and extreme users, then the usability progressively decreases.
- The method of extremes designs according to both sides of extreme users, meaning that all the average users in-between will also have high usability.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- The method of extremes encapsulates the greatest number of users, but the research can be sensitive for those in the extremes.
Observation
- A collection of responses from users, a trial or observation of users interacting with the product.
- Essentially is a user trial where the intended client uses the product and the expert observes.
- This can be in the field (natural environment) or in a lab (controlled environment).
- Observation can unveil unforeseen usability issues, as users might interact with the product in unexpected ways.
- Observations provide valuable data and feedback to refine and inform future designs.
- Cheap and readily available user trials.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- However, observation has some downsides, as a number of products need to be produced for users to test, which can be expensive.
- Interpretation of varying results can be difficult.
- Observation can be a time-consuming process that might delay entry to the market.
Interviews
- The best way to acquire information from users is to directly ask it to them.
- Interviews allow designers to gain insight on a users needs and goals which they might notice from outside observation.
- Human-centered design (not user-centered, just all designs made for humans to use) is about getting to the people you're designing for and hearing from them.
- Conducting interviews is vital to learn more about a person's mindset, behavior and lifestyle.
Focus-Groups
- You can come to a quick understanding of a community’s life, dynamics, and needs by conducting a group interview (focus group).
- Though a group interview may not offer the depth of an individual interview in someone’s home, it can give you a compelling look at how a larger set of the people you’re designing for operates.
- The best group interviews seek to hear everyone's voice, get diverse opinions and are strategic about group makeup.
- Having a diverse variety of perspectives and opinions allows for more comprehensive understanding of the users.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- It is dynamic and face to face, so gestures and reactions can be observed.
- Clarifying questions can be asked.
- Provides large amounts of qualitative data that is difficult to achieve from other forms of data collection instruments.
- Identify users' requirements more precisely.
- Designers can build a range of scenarios, personae and use cases with the data.
- Interviews can be expensive when participants are compensated.
- Some participants might not wish to share specific information.
- The participants might not be representative of the whole.
- The interviewer might influence the answers.
Questionnaires
- A research instrument consisting of a series of questions for the purpose of gathering information from respondents.
- Questionnaires can be good for getting a very large number of responses in order to get a general understanding. It is usually harder to obtain more specific information from a questionnaire.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Questionnaires are cheap and easy to administer, meaning a large number of questions can be asked.
- They can easily be sent on a local, national or even global scale.
- The questionnaires however can be static.
- They might result in a poor number of responses or biased ones.
Affinity Diagramming
- Affinity diagramming is a tool used to organize ideas and information.
- It typically involves a team gathering together, with each member writing a number of notes based on their observations and ideas. The notes are then categorized in meaningful groups.
- A visual representation of a system, and a great way to make sense of data.
- They express data and information in a common format by creating clusters and groups of common information.
- They are used to highlight key relationships and develop strategy.
- It represents a text based map which shows aspects of the product that has been/will be taken into consideration in the design and manufacturing of the product, thereby presenting the results.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Simple to undertake and cost effective way of getting data from a team and building teamwork.
- Might be time consuming if it gets too large.
Participatory Design
- Participatory design, or PD, is an approach where all stakeholders are involved in the design process.
- Traditional design projects typically include the paying client and professionals within similar and related industries.
- In participatory design, members of the wider community; from the users who are directly affected by the design, to the local business owners who may be peripheral to it, are also recognized as legitimate stakeholders with the ability to impact the project.
- Often a replica of the design is used such as a paper mock-up for the users to interact with. They can then give suggestions and criticisms.
Prototype Testing Session
- A session where a test product is made and tested.
- All experiments are conducted before making the final product, making all changes necessary that can be seen when the prototypes are used.
Testing Environments
Usability Testing Session
- The testing of a product with potential users to find out how usable the product is.
- Generally in usability testing sessions the users are seated with an instructor who guides and observes their interaction with the product.
Usability Laboratory
- A lab in which usability testing is carried out, and test users are monitored by another group of observers in a different room.
- In user laboratories, the user is instructed to perform various tasks with the product, and is observed by people behind a one-way mirror in another room, recording the activity and noting insights.
- Generally tests are recorded for later reference and analysis.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Controlled environment can ensure that product is used as intended.
- Groups of ‘observers’ can view the usability and give a more wider view of analysis.
- Labs can be set up with high-tech sensors and equipment for better monitoring.
- Can be costly as personnel must be hired.
- Can be intimidating for the tester to know people are behind one-way mirrors.
Testing House
- Typically a company that will test products on their site.
- In a testing house the company tests the product, and the user is not involved.
- Generally testing the physical capabilities.
Advantages or Disadvantages
- Can test the product under very extreme conditions, giving unbiased results.
- Doesn't test the usage by the real user.
- Mostly quantitative data is collected.
Natural Environment
- The monitoring of the user interacting with the product in their homes, place of work or other natural product usage environments.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Solicit data from real and intended contexts.
- Usability is tested in the intended environment.
- Biased opinions from the observers.
- Mostly qualitative data is collected.
Sources