What are the Scale of Production?
- Decisions on scale of production are influenced by the volume or quantities required, types of materials used to make the products and the type of product being manufactured.
- There are also considerations of staffing, resources and finance.
- The four scales of production are:
- One-off Production
- An individual (often craft- produced) article or a prototype for larger-scale production.
- Batch Production
- Limited volume production.
- A set number of items to be produced.
- Mass Production
- The production of large amounts of standardized products on production lines, permitting very high rates of production per worker.
- Mass Customization
- A sophisticated CIM system that manufactures products to individual customer orders.
- The benefits of economy of scale are gained whether the order is for a single item or for thousands.
Economies of Scale
- Large-scale production, achieved through operational and manufacturing efficiency.
- This helps in reducing the cost of production, reducing the cost per unit (cost of products manufactured).
- The more you can make, the cheaper it costs to manufacture. This results is higher profit margins and/or cheaper retail pricing for the customer.
- If you've ever wondered why larger companies can sell the same products for a lot cheaper than small local firms, it is because they have the benefits of economies of scale.
One-off Production
- In one-off production often a single product is designed and made to a client’s specification.
- Labour and material costs are high, and a high level of design and manufacturing skills are needed.
- The product is often very expensive, but can be customized and is often completely unique.
- Some one-off products might be sold by a professional or master and have unique artistic or functional qualities.
- 3-D printing makes one-off production much more accessible.
- Examples of one-off production include:
- prototypes / samples (e.g. car or clothing production)
- hand crafted items (e.g. wedding dress, jewellery, dolls, pottery, Instruments)
- specialist engineering
- specialist architecture (e.g. individual homes, skyscrapers, hotels like the Hydropolis)
- products that are generally unnecessary and too costly to mass produce, such as cruise-liners
Batch Production
- The best method of production depends on the type of product being made and the size of the market.
- Batch production is used to meet group orders.
- For example, a set of machines or production lines could be set up to make certain specific shipping containers.
Mass Production
- Mass production is used for products that are needed in very large numbers, for example electronic products.
- Often, products are made overseas where labor costs are lower and assembly lines are used.
Continuous Flow Production
- A production method used to manufacture, produce or process materials without interruption (24/7).
- Robots are used very commonly in mass production as a whole, and especially in continuous flow production.
Mass Customization
- Usually the basic form of the product is constant but by using flexible CAM systems the product can be customized in terms of color combinations, texture, patterns.
- It is a compromise between mass production and on-off/batch customization where customization is limited in order to allow for mass production to take place.
- Generally it results in some increased costs, although it is still relatively affordable.
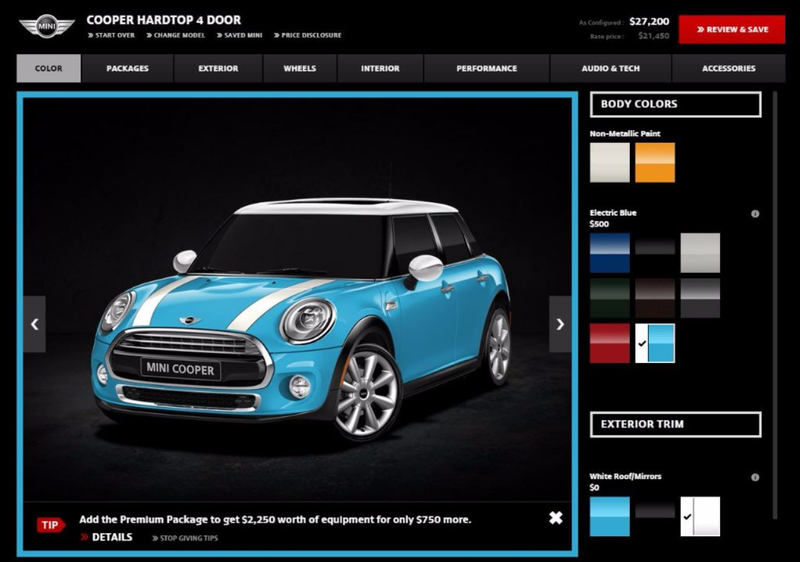
- The relationship between the manufacturer and customer becomes closer because the individual requirements of the consumer dominate.
- The mass customization process begins at a website where the user has the opportunity to choose aspects of the design.
- The idea is that the manufacturer is meeting the needs of the user although using manufacturing techniques that remain the same.
- The growing phenomenon of mass customization brings consumers into the design process, allowing them to make choices that make a product unique, to make it their own.
- Companies have developed “design stations” in their retail stores where consumers can create virtual 3D models, “try them out” using digital technology and place their order.
