Iterative Process
- An iterative process is the act of repeating a process with the aim of approaching a desired goal, target or result.
- Each repetition of the process is also called an iteration, and the results of one iteration are used as the starting point for the next iteration.
- The process of UCD is iterative, led by the user and developed through user-centred evaluation.
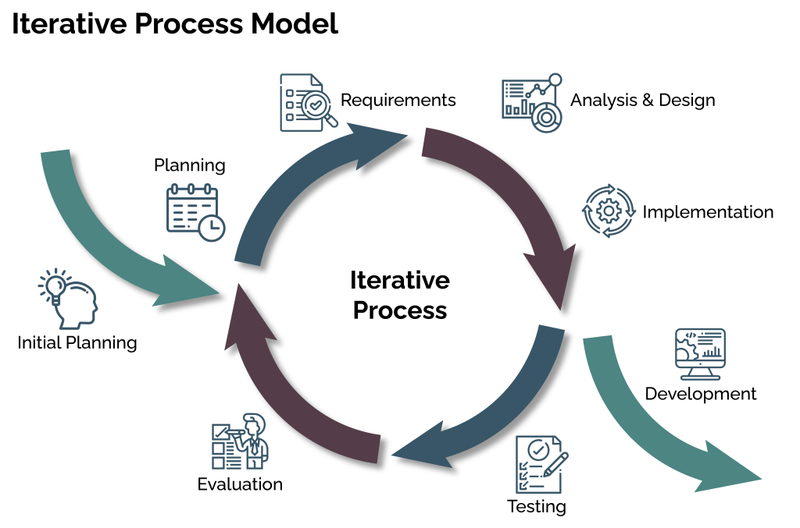
- The iterative design process is developed through user-centered evaluation and is based upon the six principles of iterative design:
- A design is based upon an explicit understanding of users, tasks and environments.
- Users are involved throughout design and development.
- The design is driven and refined by user-centred evaluation.
- The process is iterative.
- The design addresses the whole user experience.
- The design team includes multidisciplinary skills and perspectives.
User Experience
- User experience is a person's perceptions and responses that result from the use or anticipated use of a product, system or service, this can modify over time due to changing usage circumstances.
- Designers and companies have shifted from conventional market research techniques to greater emphasis on the user experience. UCD involves smaller numbers of people than conventional market research and it can lead to unexpected insights that stimulate innovation.
- Conventional market research may be flawed as users often do not tell researchers the true facts about a product or they cannot identify how and why they use products—particularly for radical designs.
- Awareness of the experience of end-users can lead designers to question established practices and assumptions. UCD enables user feedback to inform product re-development even after launch, sometimes in quite a radical way.
