Economic Viability Definition
- Economic viability is the economic feasibility of products for them to gain a place in the market.
Costing vs Pricing
- Costs is the expense that a business incurs in bringing a product or service to market. This include fixed and variable costs involved in designing and manufacturing the product, and getting it to the point of sale.
- Price is the amount a customer pays for that product or service.
- For a product to achieve profit, the price of a product has to be higher than its cost.
Value for Money
- The relationship between what something, for example, a product, is worth and the cash amount spent on it.
Cost-Effectiveness
- The most efficient way of designing and producing a product from the manufacturer’s point of view.
Costs
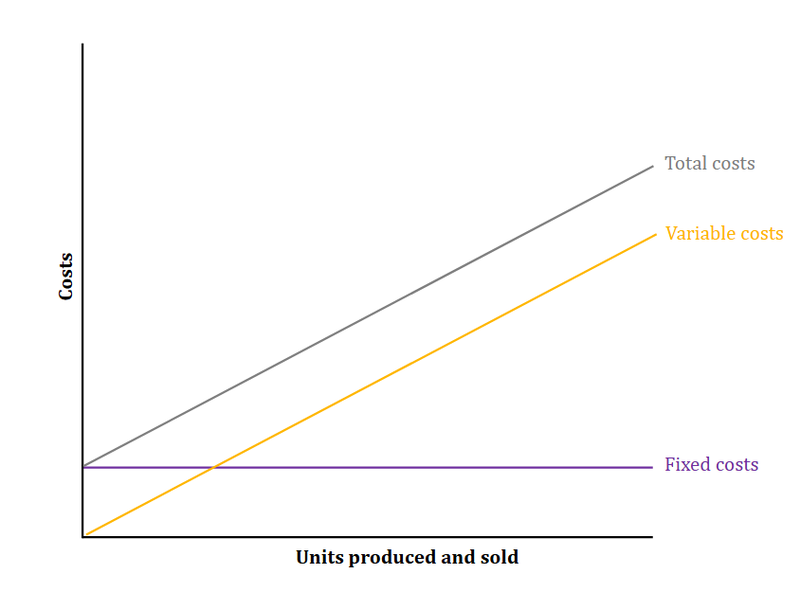
Fixed Costs
- The costs that must be paid out before production starts.
- These costs do not change with the level of production.
- For example machinery or real estate.
Variable Costs
- Costs that vary with output.
- For example fuel or raw materials.
Total Costs
- The sum of fixed and variable costs.
Unit Costs
- The costs a company incurs to produce, store and sell one product (item).
- This is calculated as an average cost.
- These include fixed and variable costs.
Sales Revenue
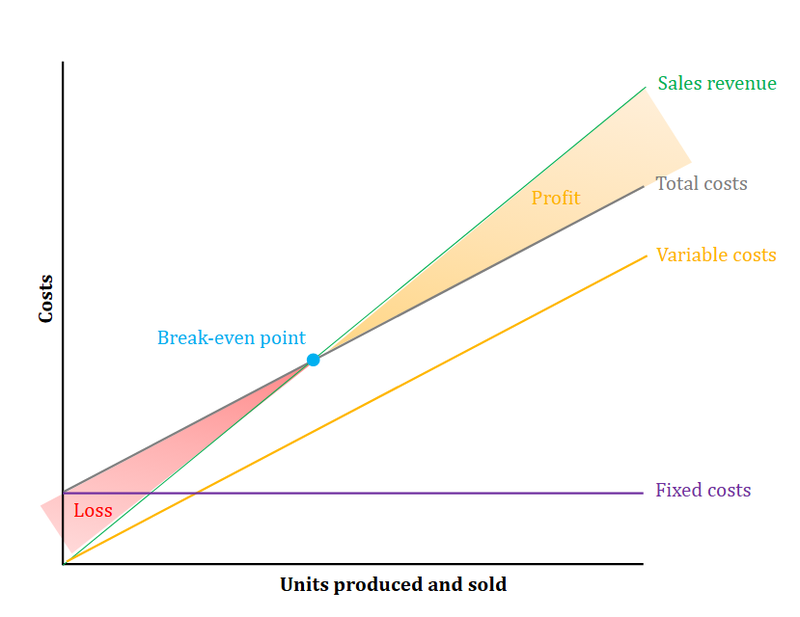
- Assuming we’ll sell each product at the same price, and that we sell everything we produce, there should be a linear correlation between the number of sales and the revenue (earnings) that it brings in.
Profit, Loss and Set-Up costs
- When the sales revenue exceed the cost of production we get a profit.
- Until that point we will be operating at a loss.
- Because of high set-up costs (fixed costs) most businesses do not make a profit until after their 5th year.
Break-Even Point
- This is the point in time when sales revenues overtake production costs and companies move from loss to profit.
Cost Analysis
- A tool used to determine the potential risks and gains of producing a product.
- It is used by manufacturers to determine the break-even point for a product and can be used to create multiple scenarios for a product.
- It allows the feasibility of a product to be established.
Pricing Strategies
Price-minus strategy
- The market demand determines the product pricing (selling price) before manufacturing begins.
- Then all commercial costs (manufacture, profits, etc) are determined and the company works within these constraints.
Retail price
- It is the recommended retail price (RRP) (more general) suggested by the manufacturer (MSRP/ specific) price that the retailer should sell the product for.
- It is to standardize prices.
- Some retailers will sell below the RRP to lure customers.
Wholesale price
- The cost of a product sold by the wholesaler.
- The product costs more than the manufacturer, but less than the retailer.
Typical manufacturing price
- It is the total costs (variable and fixed) to manufacture the product.
- Divide the total manufacturing/product costs by the total products/items produced to get the average cost/price per unit.
- Once total costs are determined then a profit margin is added.
- The goal is to maximize profit.
Target costs
- The desired final cost of a product is determined before manufacturing begins.
- This is based on the competing pricing.
- Profit is then removed to determine initial cost.
- The product is designed to meet it.
Return on investment
- ROI is about how much of what you invest in a company (buying shares or investing in new technology for the factory etc) you see back in profits at the end of the year.
- So this shows us how much profit we make for each Euro/Dollar invested in the company.
Unit cost
- The company researches the unit cost for one product in order to determine pricing.
Sales volume
- It is the amount of products sold in a specified time period during regular working operations of a company.
- They can be annual, quarterly, etc. sales.
- Can also be based on demographics, geographic regions, etc.
Financial return
- Financial return is, more generally, any money we make from a transaction.
- That could be from selling the products, selling off a piece of land or how much we make from investing in a company (as in ROI).
Economic Viability
- The economic viability of a product is paramount for designers if they are to get their product into production.
- Understanding how to design a product to specification, at lowest cost and to the appropriate quality while giving added value, can determine the relationship between what a product is worth and how much it costs.
- Designers need to consider how the costs of materials, manufacturing processes, scale of production and labor contribute to the retail cost of a product.
- Strategies for minimizing these costs at the design stage are most effective to ensure that a product is affordable and can gain a financial return.