Pioneering Strategy
- Being first to market with a new innovation.
- Generally more risky, but greater potential for market share and brand loyalty.
- Often requires a lot of investment in research and development.
- For example Apple's iPhone.
- Risk of failure is high.
- Costly, therefore the company needs to be financial secure.
- Potential for large gains.
- Requires a strong research and development (R&D) capability.
- Product champions who push new ideas are important.
- Market research is vital.
- The risk of failure is considerably high because this product or service has never entered the market, thus making it is impossible to determine that the product will be a success or failure since the product/service’s lack of experience in the market.
- Although pioneering is risky and costly, the profits that can be earned from this strategy balances out the risk factor.
Imitative Strategy
- Developing products that are similar to an existing new product.
- Less risky than the pioneering strategy but also generally less popular.
- Less research and development costs.
- An example of an imitative strategy would be the many other mobile phones that came out soon after the iPhone, which used similar components and layouts.
- It takes advantage of R&D invested by others.
- Less risky.
- Based on a strong development capability.
- The designer must consider the ethical implications of imitating the products of others and their implications on a cultural, economic, and intellectual property level.
Ansoff Matrix
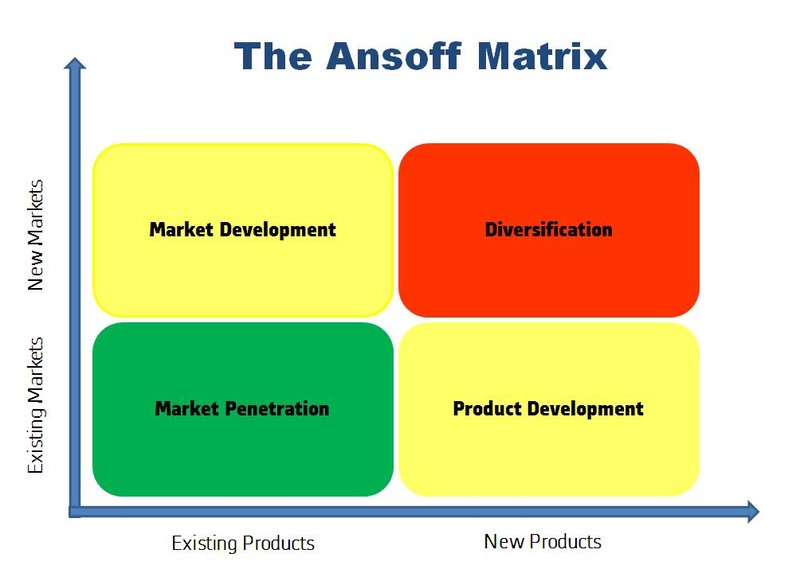
- The Ansoff Matrix is a diagram that is used to categorize the strategies of different products.
- There are four different categories that a product can be in, which are market development, market penetration, product development and product diversification.
Market Development
- Finding new applications for existing products, thereby opening up new markets.
- E.g. try to sell an existing product to a new group of consumers.
- This growth strategy is more risky than market penetration because of the fact the business is focusing on a new market which it may or may not be successful in.
Market Penetration
- Increasing sales to existing customers or finding new customers for an existing product.
- E.g successful selling of a product or service in a specific market. It is measured by the amount of sales volume of an existing good or service compared to the total target market for that product or service.
- The market penetration strategy emphasizes that organizations should focus on the markets and products they are familiar with.
- This is usually of lesser risk because the organization has an idea of the information in the market, its competitors etc.
Product Diversification
- Increasing sales from new products targeting new markets or market segments.
- E.g. new products to increase sales by reaching out to other market (segments), such as the development of the iPad, iPhone and the iPod.
- This strategy is the most risky from the four because the business is moving into a market in which it has minimum experience.
- This strategy is usually adopted by large organizations looking to expand their product portfolio and profitability through dispersing their risk in different markets.
Product Development
- The creation of new, modified or updated products aimed mainly at a company’s existing customers.
- E.g. product development to keep up to date with the demand of existing customers. Such as releasing new, improved, generations, such as the 2018 generation over the 2017 generation iPhone’s.
- This strategy requires the organisation to develop new competencies and modify products to entice people in the market.
- This type of strategy is particularly important in markets with a lot of competition because it provides the organization with a competitive advantage with the constant introduction of new products to existing customers.
Hybrid Approach
- Some companies use a mix of corporate strategies for their products.
- There are many benefits for a company using a hybrid strategy. Companies use a mixture of the corporate strategies in order to:
maximize profit and sales
reduces R&D spending
reduces the risk of employing only a pioneering strategy.
Corporate Social Responsibility
- A form of self-regulation for a company that centres on the development of goals related to three areas:
- economic (profit)
- social (people)
- environmental (planet)
- Related to “Triple Bottom Line” and ‘Sustainability report’.
- Corporate social responsibility can be a particular goal of a company.
- The aim is to manage the economic, social and environmental impacts of their operation to maximize the benefits and minimize the disadvantages.